CONCEPT OF DAIRY CO-OPERATIVE AND MILK PRODUCTION IN INDIA
Compiled by-DR. RAJESH KUMAR SINGH, JAMSHEDPUR
INTRODUCTION
Operation Flood and dairy co-operatives emerged in India as the largest rural employment scheme, enabling the
modernization of the dairy sector to a level from where it can take off to meet not only the country’s demand for milk
and milk products but can also exploit global market opportunities. This article reviews the existing status of milk
marketing and dairy co-operatives in India and provides recommendations to meet future challenges. The results of
the study indicate that 80 percent of the milk produced by the rural producer is handled by an unorganized sector and the remaining 20 percent is handled by an organized sector. It is found that the dairy co-operatives play a vital role in alleviating rural poverty by augmenting rural milk production and marketing. Involvement of intermediaries; lack of bargaining power by the producers; and lack of infrastructure facilities for collection, storage, transportation, and processing are the major constraints which affect the prices received by producers in milk marketing. Milk quality, product development, infrastructure support development, and global marketing are found to be future challenges of India’s milk marketing.
India is one of the largest milk and milk products producing countries in the world. The country‟s milk Milk and milk products are indispensable to the growth of the child and to the health of the adult. For the infant, milk is a perfect food, for the growing child, milk and the milk products of the dairy industry are essential foods, and
for adults and expectant mothers they are the most important foods. In India, it is generally observed that in the north and west the cow are better milkers, but as one gets to the south and east the milk producing quality deteriorates.
The importance of livestock sector in general and of dairying in particular hardly needs emphasis in a country like India. The major and more widely known contribution of livestock sector is in terms of production of milk and milk products. Apart from milk, this sector contributes meat, hides, skins, organic manure and draft power.
Milk production activity takes place on individual farms of varying sizes. This characteristic of milk production system coupled with perishable nature of milk imposes severe constraints on devising improved system for assembling, processing and distribution of milk and its products.
In this post, characteristics of production pattern of milk have been presented. Specially, it covers composition of milk, milk production, price scene for milk and milk products, relative importance of cows and buffaloes in milk production, production ratio and seasonal variation in milk production.
ROLE OF CO-OPERATIVE MOVEMENT IN DAIRY:-
The study of dairy activity is not complete without taking into account the co-operative movement in India. Co-operation means working together in a team for attaining certain objectives. The spirit of village communities in India was almost entirely based on the philosophy of co-operation. In the modern co-operative societies may be found at local, regional, national and international levels, where a distinction is made among them on the basis of the extent of area they cover.
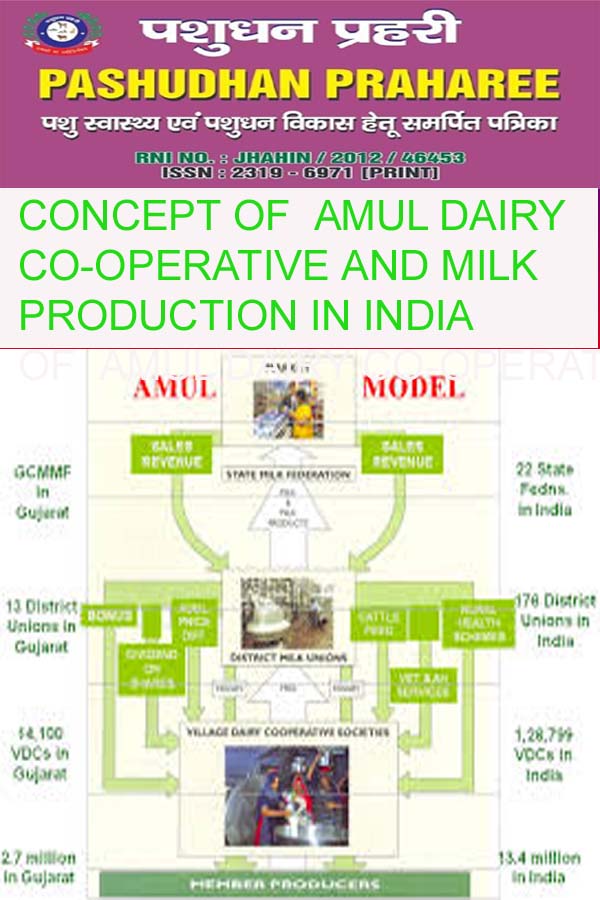
In many states of india, dairy activity is developed on co-operative basis. The keen interest of state government and support of farmers are the main reasons for co-operative dairy development in the state. The dairy activity is now largely based upon a three tier system under which, the primary village cooperative societies are linked with district union and state federation which are guided by the national co- operative dairy federation in India.
The structure of co-operative dairy is as follows –
1) The state co-operative Milk Federation Ltd at the top level.
2) District or Taluka co-operative Milk Federation at district level.
3) Primary co-operative Milk producing societies at village level.
MILK COLLECTION:-
Dairy activity practiced everywhere in the district level. The primary milk societies collect milk in village level and supply to the dudh sangh in the district level. This point includes the distribution of dudh sangh and milk collection at the district
OBJECTIVES OF DAIRY COOPERATIVES IN INDIA
• To bring the unorganized dairy sector into the fold of organized sector.
• To improve input activities and animal health care for increasing milk production • To encourage liquid milk availability.
• To tap the milk potential of the State and to ensure stable growth in procurement and Marketing. • To ensure quality of milk and milk products as per the statutory specification.
• The major, supervise and regulate the dairy activities.
DAIRY COOPERATIVES IN INDIA-AN OVERVIEW
Annual milk production in India has more than tripled in the last three decades. This rapid growth and modernization is largely credited to the contribution of dairy co- operatives under the Operation Flood (OF) Project, assisted by many multi-lateral agencies including the European Union, the World Bank, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), and World Food Program (WFP), despite the impressive growth in milk production in the last three decades, productivity of dairy animals remains very low and milk-marketing systems primitive. Currently, more than 80 percent of the milk produced in the country is marketed by unorganized sectors and less than 20 percent by the organized sector. The organized sector involves government and co-operatives; the unorganized sector involves private organizations.
The role of dairy cooperatives in procurement of milk and providing necessary services to the dairy farmers make them distinct among the other channels of milk marketing. The dairy farmers selling the milk to the dairy cooperatives get fair prices of their product. These centres also provide financial security and give the money to the dairy farmers at certain intervals. Thus the dairy farmers get a consolidated amount from the dairy cooperatives. The major constraint with this channel is delay in payments by the dairy cooperatives. The poor households are unable to wait for longer periods to get the payments and thereby prefer to transact their marketable surplus through other channels.
The important role played by dairy farming in the sustenance of landless and poor people in the village
economy is quiet evident. Marketing of milk through organized sector involves government and co-operatives
agencies while the unorganized sector involves the private organizations. Major part of milk is marketed
through the unorganized sector and the organized sector has a very low share. The government of India has
started the “operation flood” programme for the proper enumeration of milk & milk products (George S.,
1987). Further, various programs were undertaken for the formation of dairy co-operatives. The dairy
co-operatives in India have three tier of structure which consists of state level federations, district milk unions and dairy co-operative societies at the village level respectively. As a result, dairy co-operative societies have been formed to meet local demand for milk & to eradicate the existing malpractices in the milk marketing. A substantial amount of money has been spent on the formation of dairy co-operatives to provide the infrastructure for dairy co-operatives. The evolution of dairy co-operatives has fuelled empowerment of rural people and promotes rural development.
PROBLEMS AND PROSPECTS
Dairy co-operatives should play a commendable role in future in regenerating the rural life. The need
of the hour for the Cooperative sector in the era of liberalized environment is to seize every opportunity
available. The Major problems faced by Cooperatives are: Inadequate support from government, Low
capacity utilization of dairy plants, Non-viability due to losses, Lack of working capital, Inappropriate
marketing strategy to meet competition due to lack of training and knowledge. Government should provide
technical and financial support to dairy cooperatives in the areas of strengthening cooperative business,
productivity enhancement, quality assurance, building dairy infrastructure and for creation of a national
information network by developing various schemes such as Dairy Venture Capital Fund (DVCF)/Dairy
Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS) an a large scale. Automatic Milk Collection Unit (AMCU)
and Bulk Milk Cooler (BMC) at grass root level to preserve quality and reduce post-procurement losses.
CONCLUSION
The diary co-operatives have to play a major role in our nation‟s economy in the years to come. The milk prediction is set to achieve a new boom. The industry‟s major contribution in providing newer avenues for employment, both direct and indirect, and its role in improving the nutritional standards of our people also add to the importance that needs to be attached to this sector in the 21st century. With proper encouragement and member support, cooperative can scale new heights in the near future.