HEALTH CARE MANAGEMENT OF GOATS FOR BETTER PRODUCTION
Health management is an important and integral part in goat farming. Through goat management, it is necessary to improve the productivity of goats, such as: general health management, parasite control, vaccine management, environment management and proper record keeping. Health management in farm level includes proper care taking of health of pregnant doe, newborn kids, youth and adults. Similarly, health management help to reduce the mortality rate of newborn kids, and it provides knowledge, skill and practice of control of infectious diseases.
‘Prevention is better than cure’, the statement best fits for livestock too. In healthy livestock, better immunity and recovery is quicker. But, if livestock fall sick, farmer must buy medicines, and it increases cost also. Treatment of disease must be faster; otherwise it will be very difficult to treat.
Methods of recognizing sick and ailing goats
Ailing goats show different symptoms as per the nature of diseases. But, normally sick goat shows as followings:
- Droopy, poor or no appetite
- Stays aloof from herd
- Loss of smartness and hair get risen, standing hunch
- Coarse and dull skin
- Low physical growth rate
- Red eye, runny and watery eyes
- Pulse speed (it can be felt by touching interior side of rear thigh), breathing, variant temperature than usual and stinking breathing
- Loose feces, mixed with blood or mucus
- Dark yellow pee and sometime blockage of urine,
- Floating saliva from mouth
Tasks to keep the goats healthy
- Feed adequately and quality feeds along with clean water
- Know major diseases and vaccinated against those diseases
- Control of internal and external parasites
- Keep ailing goat/s separately and do not mix with healthy goat/s
- Thoroughly screen at the time of bringing new livestock/goat
- Construct good shed to protect from unsuitable climate
Major diseases in goats
- Bloat in goat
Causes:
- By overeating damp and very old fodder
- By overeating legume pastures or crops
- By overfeeding the concentrate feeds
- Symptoms:
- In the beginning of this disease, seems depressed, loss of appetite and bulging starts from left flank of belly,
- Difficulty in breathing, striking legs, bleating,
- In some cases, goat death is found in pasture
- Treatments:
- Hold frontal legs of goat and massage in left flank of belly
- Drench oil or feed paraffin liquid to goat
- Contact to technician if these treatments do not heal
- Do not feed more crops or leguminous forage to goat
Diarrhea (Loose feces)
- Causes:
- Small kids usually get
- Causes of diarrhea are consuming impure milk, too much milk or
- Certainly, changes in environment may also cause
- Diarrhea can also be caused by virus and internal parasites
· Symptoms:
- Looks like in pain in belly, not interested in feeding and watery feces
- If diarrhea persists for long time, body may go with dehydration, cannot stand, and goat’s eye and temple get sunken
· Treatment:
- Diagnose the real diseases and do the treatments accordingly,
- Goats are in dehydration, so feed enough water and If necessary, give intravenous treatment by giving saline water.
- If it is due to cause of virus, then as per advice of technician, medication to be
Pneumonia
- Causes:
- Virus, Bacteria, parasites and environmental effects
- Symptoms:
- Droopy goat/s in the beginning
- Raised temperature-fever and coughing
- Dark discharge from nose
- Difficulty in breathing and fast breathing
Treatment and control:
- With the help of technician, administer injection of antibiotic
- Keep separately the sick goat/s from herd
- Manage transportation of goats with less stress
- Keep shed dry and cover with jute sacks in cold
Hoof rot
- Cause:
- Hoof rot disease is caused by bacterial
Symptom:
- Goat’s hoof becomes painful due to which doe’s do not get proper growth and buck has difficulty in
- Suddenly goat starts limping at the beginning and inflammation between hooves start.
- There is wound inside hooves and goat cannot stand.
Treatment:
- Separate sick goat from other herd and pay attention in maintaining
- Use soap or iodine for cleansing infected
- Use antibiotic as per recommendation of
Importance of trimming hooves and trimming methods
- Time to time hoof should be trimmed, as when it gets longer, it gets rotten and difficult to move around for those goats which are reared in stall-fed, rather than goats in grazing
Hold goat tightly and make immovable
- Check the color of hoof, whether it is rotten or not,
- Cleanse dirt from the hooves,
- Trim small upper tip of hoof,
- Trim the tip of hooves maintaining the level (like people’s nail)
- Trim more slightly interior part of hooves than the outer
Attention be given to health of goats
- It is necessary to have update information of the health of livestock and nutrition status
- Information on goat’s health can be learnt by observing its physical condition
- By observing goat’s teeth, age of the goat can be assessed and according to the age of goats, physical condition of goats can be known
- Similarly, by observing eyes of goat, quantity of bloods in body can be known,
- By observing feces of goat, information on health condition can be known
- Observation of healthy goats
Whether goat has anemia or not, can be identified observing the goat’s eye (mucus membrane). The methods of identifying the condition of goats from color of eyes are as followings:
- Dark pink color: adequate condition
- Pink color: Not anemic
- Light pink color: Guess for anemic
- More Light Pink color: Anemic and needs urgent treatment
Teeth condition of goats based on its age
| SN | Age | Teeth | Figure of teeth |
| 1 | 6 to 10 month | Incisors-8 front side milky teeth | 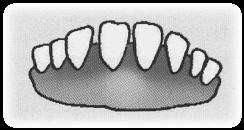 |
| 2 | 10 to 14 month | 2 frontal fixed and 6 milky teeth | 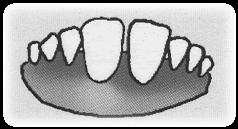 |
| 3 | Age of 2 years | 4 frontal fixed and 4 milky teeth | 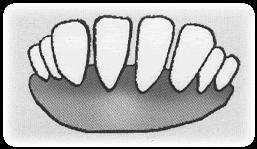 |
| 4 | Age of 3 years | 6 frontal, fixed and 2 milky teeth | 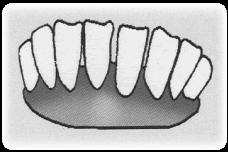 |
| 5 | Age of 4 years | 8 frontal, fixed teeth | 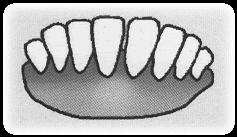 |
| 6 | Age of above 6 years | Grind and loosened Frontals, fixed teeth | 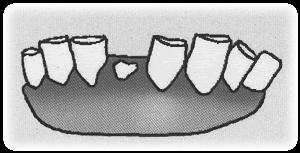 |
Fig. Condition of goat teeth based on age
Parasite control and vaccination for infectious disease
- Parasites
- Parasites live on nutrition from
- Internal parasites live inside goat’s
- External parasites live outside goat’s
- The parasites attack on healthy But, if the parasites attack in big scale, the goats fall sick and sometimes may die of it.
Internal parasites
- Stomach worms
- Cause:
- Goats having eaten contaminated feeds, water, grasses or fodders with eggs of worms or such worms are developed through infection in healthy goats
- Stomach worms grow in shape like earthworm
- Symptom:
- There is no appetite in feeds, any speedy growth, droopy, rough skin and loss of hair coat to goat.
- Sometimes feces seem normal and sometimes loose (watery feces).
- While touched, the belly feels
- It is stinking
Lungworm
- Cause:
- It is developed if goat eats grass with the eggs of lung
- Symptom:
- Weight loss in goat, droopy, loss of appetite, yellow eyes (anemic)
- Sometimes watery feces, sometimes constipation symptoms
- Dull skin
- Swollen jaw
- Treatment and control
- Albendazole: feed 15 mg. / kg as per body weight. But, it should not feed to pregnant doe or
- Oxyclozanide: 15 mg/kg as per body weight of goat or
- Fewendazole: 5 mg/ kg as per body weight of goat or
- Levamisole: 8 mg/kg as per body weight of goat or
- Ivermectin: 0.2 mg/kg as per body weight of goat inside skin administered through injection
Tape worm
- Cause:
- In goat’s feces of infected with tape worm, eggs and small pieces of worms drops on ground; such particles may be swallowed with grazing grasses by livestock; and reach to stomach and intestines and such tape worms is
- Symptom:
- Anemia
- Weight loss
- Constipation in defecation
- Seen tapeworm in size of rice piece in feces of goat
- Treatment and control
- Praziquantel: 5 mg/kg feed goat as per body weight or
- Pyrental: 10 mg/kg feed goat as per body weight
External Parasites
- Cause:
- The following problems are seen in goats, livestock and bird due to external parasites
- Symptoms:
- Scabies
- Anemia,
- Weight loss
- Treatment:
- Dipping: Soak sick goat (protecting nose, eyes and mouth) in the mixture of dipping tank with prepared medicine of 1000 parts water and 3-5 parts of Malathene or Saythene,
- Control external parasites like lice, tick, mites, fleas, flies
Avermectin: 0.2 mg/kg as per weight of goat’s body administered through injection deep in skin
Importance of immunization and schedule
Proper immunization will help in having good health of livestock. Vaccines will help to promote immunizations in livestock, therefore timely vaccination is required.
Vaccination schedule for goat
| SN | Name of disease | Time for vaccine | Interval for vaccine |
| 1 | PPR | After 3 months old | Once in every 3 years |
| 2 | Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) | After 4 months old | Once in every year |
https://www.pashudhanpraharee.com/heat-stress-and-its-management-in-goat/
PPR
- Cause
- This disease is caused by viruses
- Symptoms
- Goats are in fever from 106˚ to 108˚ Fahrenheit (use thermometer for measurement)
- Goats do not eat fodder and water; and eyes get
- Sore will start affecting gum and tongue; and slowly covers in
- Difficulty in breathing process
- Feces get watery and sometimes mixed with blood and mucus; death at the end
- Treatment and Control
- There is no effective treatment of PPR, therefore it is wise to be attentive and start prevention on time.
- Sick goat needs to be isolated from other herd to prevent from infection from one goat to another,
- Discard all matters and materials used to treat sick goat or purification
- Dig deep hole to put with adequate lime and salt together with carcass of infected goat and cover the hole
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD):
- Cause:
- FMD is caused by viral infection in goats. It affects less compared to cow, buffalo and pig. But, if the goats are severely affected, it can cause abortion, feeding difficulty and walking difficulty in goats
- Symptoms:
- Fever
- Salivate
- Lost appetite
- Munching mouth
- Red sore in between hooves and lameness
- Swollen tongue and abscess
- Treatment and control
- Cleanse sore of mouth with salty solution, zinc or copper sulfate solution
- Cleanse wound of legs with phenol liquid and put hymex ointment
- Isolate sick goat from herd
- Annually vaccinate goats
- DR DEEPAK SINHA, LIVESTOCK CONSULTANT, PATNA


