Detailed Project Report (DPR ) for establishment of a New Bulk Milk Chilling (BMC ) Unit for Dairy Cooperatives in India
Bulk Milk Cooling Units
- Indian dairy industry is contributing significantly to the country’s economy, besides improving the health standard by increasing the nutritional value of the food. India occupies first position in the world milk production with 19% share of in global milk output.
- As per 19th Livestock census, 2012, the country has about 190.90 million cattle (122.98 million female cattle) and 108.7 million buffaloes (92.6 million female buffaloes). Breedable female cattle and breedable female buffaloes account for 76.685 million (21.268 million crossbred cattle and 55.417 million indigenous cattle) and 56.586 million numbers, respectively.
- Recognizing the importance of the sector, the notable programmes taken up by GOI are key village schemes, intensive cattle development projects, crossbreeding projects through bilateral assistance, Operation Flood programme, Technology Mission etc. Most of the milk in the Country is produced by small, marginal farmers and landless labourers. About 15.1 million farmers have been brought under the ambit of 1,55,634 village level dairy corporative societies up to March 2013. The cooperative milk unions procured an average of 32.8 million kgs of milk per day during the year 2012-13 as compared to 28.7 million kgs in the previous year recording a growth of 14.3 percent. The sale of liquid milk by cooperative sector reached 23.7 million litres per day during the year 2012-13 registering a growth of 3.7% over the previous year.
- For strengthening the efforts of the dairy cooperatives to increase productivity and income of the milk producers/farmers through improved management of breeding and feeding, Government implemented the National Dairy Plan (Phase-I). National Dairy Plan Phase I (NDP I) is a Central Sector Scheme for a period of 2011-12 to 2018-19. NDP I will be implemented with a total investment of about Rs. 2242 crore. NDP I will focus on 18 major milk producing states namely Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Telangana, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh which together account for over 90% of the country’s milk production. Coverage of NDP I will however be across the country in terms of benefits accruing from the scheme.
- National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development (NPBB&DD) : The Scheme titled “National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development” (NPBB&DD) was launched on 27.02.2014 by merger of four ongoing schemes viz. Integrated Dairy Development Programme (IDDP), Strengthening Infrastructure for Quality & Clean Milk Production (SIQ-CMP), Assistant to Cooperatives (A to C) and National Project for Cattle & Buffalo Breeding (NPCBB). NPBB&DD will have two components (a) National Programme for Bovine Breeding (NPBB) and (b) National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD). A budgetary provision of Rs1,800 crore has been made for implementation the scheme during 12th Five Year Plan (2012-17). Milk chilling capacity of 1,705 TLPD and 1844 TLPD was created during 2012-13 and 2013-14 in Cooperative dairy sector.
- As per APEDA, the export of dairy products (Butter, butter oil, cheese, butter milk, skimmed milk powder, milk for babies, whole milk and ghee) was to the tune of 1.59 lakh MT valued at Rs 3318.5 crore during 2013-14 to Bangladesh, Egypt, UAE, Algeria, Yemen and Pakistan.
- Having made a significant stride in production and processing, efforts have to be directed to provide hygienically safe milk and milk products to the consumers. In addition to fat and SNF, the bacteriological quality has also be taken into account for determining quality of the milk. Therefore, emphasis has to be on veterinary support infrastructure and strengthening cold chain for quality milk production. As per Codex Alimentarius, immediately after milking, the milk must be cooled preferably to 4° C. This requires mechanical refrigeration or milk cooling tanks. It is important to remember that under a hot environment milk will spoil within 3-4 hours. So cooling will lower the temperature of milk to prevent multiplication of bacteria. Further, when milk for further processing is not used within 2 hours after milking, it shall be cooled to a temperature cooled to or below 4° C.
- The best alternative to the present collection system of milk is cooling of milk immediately after milking by Bulk Cooling Tanks. The usage of such tanks has become popular and is on the rise as it helps in increasing the shelf life of milk, facilitates systematic and simple way of milk procurement and ensures procurement of more milk by covering untapped farther areas for Milk Collection. Further the efforts are aimed at setting up of collection centres along milk routes to increase procurement in the organized sector and to facilitate scientific handling of milk as per quality norms.
- NABARD has been actively involved in credit planning, fixation of unit costs and promoting credit flow for various investments under dairy sector. NABARD is also acting as the nodal agency for implementing the credit linked Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS) of Got of India for routing of subsidy admissible (25 % or 33.33%) under the scheme. Purchase of Milking Machine/ Milko testers/ Bulk Milk Cooling Units up to 5000 LPD capacity is one of the eligible activity under the scheme.
Objectives of bulk milk coolers
The financial assistance is extended for purchase of bulk milk coolers with the following objectives.
- To arrest bacterial growth, retain freshness and enhance the keeping quality of milk
- To avoid economic losses to the producers due to spillage/ curdling of milk.
- To make available quality milk for production of quality products for export as well as to meet the domestic requirements.
- To reduce the transportation cost by regulating transportation of the milk on alternative days or once in day for two collections and also through reduction in expenditure on purchase and maintenance of cans.
- To ensure clean milk production
Potential areas
Bulk Milk Cooling Units are now taken up in all parts of the country. The scheme has potential to finance in Operation Flood programme (OFP) and also in non-OFP districts under Govt., private and cooperative sectors.
Beneficiaries
Village Milk Cooperative Societies of Cooperative Milk Unions or Milk Collection Centres of private Dairies or units. Producer Companies and SHG Federations. Individuals in tie up with private dairies can also take up the activity.
The bulk cooling units are also considered as part of large dairy farms and processing units.
Project Details
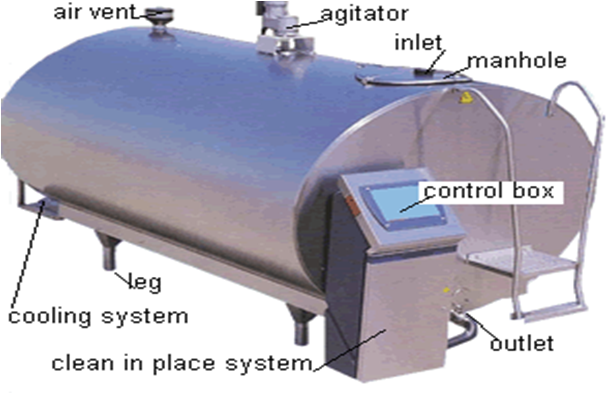
Components: The components of Bulk Milk Cooling Unit comprises of bulk cooling tank with accessories, DG set, weighing machine, weighing bowl, roller conveyor, can wash tub, Automatic Milk Collection Unit (AMCU), water storage tanks etc.
Capacity :The capacity of Bulk Milk Cooling Units is ranging from 500 to 10000 litres.
Specifications: The specifications of different models manufactured by two firms are
| Particulars | Mahesh Engineering | De Laval Pvt Ltd | ISF | ||
| BI-DX-HCL | Dx5000 | 3000 | 5000 | ||
| 1 | Basis of Design | ISO 5708 | ISO 5708 | ISO 5708 | ISO 5708 |
| 2 | Types of Cooling System | Direct | Direct | Direct | Direct |
| 3 | Shape of Tank | Horizontal Semi-cylindrical | Closed Horizontal cylindrical | Closed Horizontal cylindrical | Closed Horizontal cylindrical |
| 4 | Compressor type | Hermetic | Scroll | Scroll | Scroll |
| 5 | No.of compressors | One | Two | Two | Two |
| 6 | No.of fans | Two | Four | Four | Four |
| 7 | Power supply | single/Three phase 415V | Three phase 425V, 50Hz | Three 415V, 50HZ | Three phase 415V, 50Hz |
| 8 | Connected load | 4.96 kw | 13 kw | 9 kw | 13 kw |
| 9 | Voltage stabilizer | 10 KVA | 25 KVA | 25 KVA | 25 KVA |
| 10 | Temperature | From 35C to 4 C | From 35C to 4 C | From 35C to 4 C | From 35C to 4 C |
| 11 | Cooling time | 3 hours | 3 hours | 3 hours | 3 hours |
| 12 | Diesel Generator | 15 KVA | 25 KVA | 25 KVA | 25 KVA |
Equipment suppliers: The machinery should confirm to the BIS standards and are presently manufactured in the country by DeLaval Pvt Ltd, IDMC, IFS Industries Pvt Ltd,etc. The addresses of few manufacturers are
List of major suppliers of Bulk Milk collers
- DeLaval Pvt Ltd A-3 Abhimahshree society, pashan Road Pune – 411008, Maharashtra, India
- Indian Dairy Machinery Company Ltd. GIDC Estate Vithal Udyognagar – 388121 Gujarat, India
- New Dairy Engineering and Trading Company Pvt Ltd. B-8/5, Badli Industrial Estate Phase I, Delhi – 110042, India
- IFS Industries Pvt Ltd 88 & 90 Madavilakkam village Thriumazhisai, poonamalle Tq Chennai – 600123
- Indo Stainless Fabtech (Pvt.) Ltd. No 439 SIDCO Industrial Estate Ambattur Chennai – 600098
- Mahesh Engineering works G-10 Ravi Estate Rustam, Milk compound Near Torrent power Itd Dudeshwar Road Ahmedabad – 380004, Gujarat
Processing: The operations involve collection of milk and chilling to a temperature of 4 degree C.
Advantages:
- Elimination of souring/curdling of milk due to cooling at the collection centre itself.
- Adulteration of milk and spillage from cans can be eliminated during transport.
- Transportation cost of milk can be brought down by regulating transportation to the main dairy either on alternative days or once in a day.
- Saving of initial investment on purchase of cans and subsequent maintenance cost (Repairs, cleaning etc.).
- Improved quality of milk can be supplied to the main dairy to manufacture quality products for domestic as well as export markets.
- Flexibility in milk collection time results in increase in volume of milk collected at the centres.
- Farmers will get better returns for the quality of milk.
- Chilling at the Main dairy can be avoided.
Technical Collaboration
Since the process is simple no technical collaboration is envisaged for the project, however the Milk Unions/Private Dairy Plants would be providing guidance to the societies/collection centres in purchase and installation of Bulk Milk Coolers, milk testing and in training of manpower in the operations and maintenance.
Capital Cost
The capital cost varies with the capacity and the specifications of the Bulk Milk Coolers. However, two models have been considered i.e. 2000 and 5000 litres capacity, whose unit costs are Rs. 11.80 lakhs and 17.25 lakhs respectively. The detailed unit cost is given in the Annexure I. It is assumed that the space available in the existing collection centre/cooperative society will be sufficient to install the equipment and accordingly no cost on civil structures is considered. In case if the civil structures are required to be considered, the same may be included under project cost. Similarly rental accommodation could also be explored. Constructed area of about 800 to 1200 sq.ft is sufficient.
Backward and forward linkages
The location of the Bulk Cooling unit should be in milk shed area having potential for milk procurement. Proper arrangements for milk procurement from farmers to the unit through milk routes or alternate means have to be taken care. Regular supply of utilities such as power, fuel and water have to be ensured. Availability of man power in terms of operator, tester, workers, incharge , etc. is to be ensured.
Economics of the project
Based on the various techno economic parameters, the economics of the project has been worked out and presented below for two different models. The items of income include saving due to reduction in souring/curdling of milk, reduction in spillage and pilferage of milk, payment received for chilling, saving in repairs and replacement of cans, saving in expenditure on transportation, etc. The components of expenditure include transport expenses from society to BMCU, power and fuel expenses, repairs and maintenance, manpower, miscellaneous expenses, etc.
Financial Analysis
The income and expenditure details for two models are presented in below table:
Income and expenditure – Bulk Milk Cooling Unit (2000 lit./unit)
| Sl. No | Particulars | Years | ||||||||
| I | II | II | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | IX | ||
| Milk procurement (in litres/day) | 1200 (for six months) | 1400 | 1600 | 1800 | 1800 | 1800 | 1800 | 1800 | 1800 | |
| A. Income | ||||||||||
| 1 | Saving due to reduction in souring and curdling of milk (@ 1%) | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 |
| 2 | Reduction in spillage at 1% of milk | 0.61 | 1.53 | 1.74 | 1.84 | 1.84 | 1.84 | 1.84 | 1.84 | 1.84 |
| 3 | Payment received from milk union for chilling (@Rs1.30/litre) | 2.84 | 7.12 | 8.07 | 8.54 | 8.54 | 8.54 | 8.54 | 8.54 | 8.54 |
| 4 | Saving in repairs and replacement of cans @ Rs 0.12 /litre | 0.26 | 0.66 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| 5 | Net saving on transportation cost of milk @ Rs.0.18 / litre | 0.39 | 0.99 | 1.12 | 1.18 | 1.18 | 1.18 | 1.18 | 1.18 | 1.18 |
| B | Total Income | 4.26 | 10.68 | 12.10 | 12.81 | 12.81 | 12.81 | 12.81 | 12.81 | 12.81 |
| C. Expenditure | ||||||||||
| 1 | Milk transportation expenses from society to BMCU (Rs 0.65 /lit) | 1.42 | 3.56 | 4.03 | 4.27 | 4.27 | 4.27 | 4.27 | 4.27 | 4.27 |
| 2 | Power and fuel consumption (Rs. 0.35/litre) | 0.76 | 1.92 | 2.17 | 2.30 | 2.30 | 2.30 | 2.30 | 2.30 | 2.30 |
| 3 | Repairs and maintenance (@ Rs.0.05 / litre) | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 4 | Man power cost (Rs.0.30/litre | 0.66 | 1.64 | 1.86 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 |
| 5 | Miscellaneous expenses (Rs 0.08/lit) | 0.17 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| D | Total Expenditure | 3.12 | 7.83 | 8.87 | 9.40 | 9.40 | 9.40 | 9.40 | 9.40 | 9.40 |
| E | Gross surplus (B-D) | 1.14 | 2.85 | 3.23 | 3.42 | 3.42 | 3.42 | 3.42 | 3.42 | 3.42 |
Income and expenditure – Bulk Milk Cooling Unit (5000 lit./unit)
| Sl.No | Particulars | Years | ||||||||
| I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | IX | ||
| Milk procurement (in litres/day) | 3000 (for 6 months) | 3750 | 4250 | 4500 | 4500 | 4500 | 4500 | 4500 | 4500 | |
| A. Income | ||||||||||
| 1 | Saving due to reduction in souring and curdling of milk (@ 1%) | 0.38 | 0.96 | 1.09 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 1.15 |
| 2 | Reduction in spillage at 1% of milk | 1.53 | 3.83 | 4.34 | 4.60 | 4.60 | 4.60 | 4.60 | 4.60 | 4.60 |
| 3 | Payment received from milk union for chilling (@Rs1.30/litre) | 7.10 | 17.79 | 20.17 | 21.35 | 21.35 | 21.35 | 21.35 | 21.35 | 21.35 |
| 4 | Saving in repairs and replacement of cans @ Rs 0.12/litre | 0.66 | 1.64 | 1.86 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 | 1.97 |
| 5 | Net saving on transportation cost of milk @ Rs.0.18 / litre | 0.98 | 2.46 | 2.79 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.96 |
| B | Total inome | 10.65 | 26.69 | 30.25 | 32.03 | 32.03 | 32.03 | 32.03 | 32.03 | 32.03 |
| C. Expenditure | ||||||||||
| 1 | Milk transportation expenses from society to BMCU (Rs 0.65 /lit) | 3.55 | 8.90 | 10.08 | 10.68 | 10.68 | 10.68 | 10.68 | 10.68 | 10.68 |
| 2 | Power and fuel consumption (Rs. 0.40/litre) | 2.18 | 5.48 | 6.21 | 6.57 | 6.57 | 6.57 | 6.57 | 6.57 | 6.57 |
| 3 | Repairs and maintenance (@ Rs.0.05 / litre) | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
| 4 | Man power cost (Rs.0.38/litre | 2.07 | 5.20 | 5.89 | 6.24 | 6.24 | 6.24 | 6.24 | 6.24 | 6.24 |
| 5 | Miscellaneous expenses (Rs 0.08/lit) | 0.44 | 1.10 | 1.24 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.31 | 1.31 |
| D | Total Expenditure | 8.52 | 21.35 | 24.20 | 25.62 | 25.62 | 25.62 | 25.62 | 25.62 | 25.62 |
| E | Gross surplus (B-D) | 2.13 | 5.34 | 6.05 | 6.41 | 6.41 | 6.41 | 6.41 | 6.41 | 6.41 |
Financial analysis covering the Benefit Cost Ratio (BCR) Net Present Worth (NPW) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
For the models of 2000 litres and 5000 litres, the BCR, NPW and IRR worked out to 1.074 :1 and 1.092:1; Rs. 3.548 lakhs and Rs.10.857 lakh and 25.57 % and 36.57%, respectively. The entire bank loan can be repaid in nine/ Eight years without any grace period as per the repayment schedules presented in below tables:
Repayment schedule – Bulk Milk Cooling Unit of 2000 liters
| Year | Bank Loan Beginning | Outstanding End | Gross surplus | Payment of interes | Repayment of principal | Toral repayment | Net Available | DSCR |
| 1 | 9.424 | 9.424 | 1.14 | 0.848 | 0 | 0.848 | 0.29 | 1.339 |
| 2 | 9.424 | 8.924 | 2.85 | 1.131 | 0.5 | 1.631 | 1.22 | 1.746 |
| 3 | 8.924 | 8.174 | 3.23 | 1.071 | 0.75 | 1.821 | 1.41 | 1.772 |
| 4 | 8.174 | 7.174 | 3.42 | 0.981 | 1 | 1.981 | 1.44 | 1.772 |
| 5 | 7.174 | 5.974 | 3.42 | 0.861 | 1.2 | 2.061 | 1.36 | 1.658 |
| 6 | 5.974 | 4.724 | 3.42 | 0.717 | 1.25 | 1.967 | 1.45 | 1.737 |
| 7 | 4.724 | 3.224 | 3.42 | 0.567 | 1.5 | 2.067 | 1.35 | 1.653 |
| 8 | 3.224 | 1.724 | 3.42 | 0.387 | 1.5 | 1.887 | 1.53 | 1.810 |
| 9 | 1.724 | 0 | 3.42 | 0.387 | 1.724 | 2.111 | 1.31 | 1.618 |
| Avg DSCR | = | 1.673 | ||||||
Repayment schedule – Bulk Milk Cooling Unit of 5000 liters
| Year | Bank Loan Beginning | Outstanding End | Gross surplus | Payment of interest | Repayment of principal | Total repayment | Net Available | DSCR |
| 1 | 13.792 | 13.542 | 2.13 | 1.241 | 0.25 | 1.491 | 0.64 | 1.428 |
| 2 | 13.542 | 12.542 | 5.34 | 1.625 | 1 | 2.625 | 2.71 | 2.034 |
| 3 | 12.542 | 11.042 | 6.05 | 1.505 | 1.5 | 3.005 | 3.04 | 2.013 |
| 4 | 11.042 | 9.292 | 6.41 | 1.325 | 1.75 | 3.075 | 3.33 | 2.083 |
| 5 | 9.292 | 7.292 | 6.41 | 1.115 | 2 | 3.115 | 3.29 | 2.056 |
| 6 | 7.292 | 5.292 | 6.41 | 0.875 | 2 | 2.875 | 3.53 | 2.228 |
| 7 | 5.292 | 2.292 | 6.41 | 0.635 | 3 | 3 | 3.41 | 2.135 |
| 8 | 2.292 | 0.002 | 6.41 | 0.275 | 2.29 | 2.565 | 3.84 | 2.497 |
| Avg. DSCR | = | 2.059 | ||||||
Financial Assistance
Bulk Milk Cooling units of various sizes are eligible economic activities for loan from banks and refinance support by NABARD. The banks may consider financing for this activity subject to technical feasibility, financial viability and bankability.
Lending terms and other requirements
- Margin Money: The society or Milk collection centre should normally meet 20% of the project cost
- Interest rate: Interest rate will be as determined by the financing bank. For working out model ,the rate has been considered at 12 percent.
- Security: As stipulated by the RBI
- Insurance: The financing bank may ensure that the society takes adequate insurance cover for the asset
- Repayment period: Depends upon the gross surplus generated, it may be upto 8 -9 years without any grace period
Special terms and conditions
The special terms and conditions of the project are given in below table:
The financing bank may ensure that:
- The milk union/ dairy identifies the societies/ milk collection centres whose milk collection is about 1400-1800 litres and 3000-4000 litres per day for installing 2000 litres & 5000 litres capacity bulk milk cooling units taking into consideration of the likely acceptance of the dairy farmers for the shift in the system.
- The union/ dairy guides the society for purchase and installation of BMCU.
- The union/ dairy imparts training to the secretary and other staff of the society/ milk collection centre in the operation and maintenance of BMCU and in testing of milk
- The society/ milk collection centre enters into an annual contract with the equipment supplying firm for maintenance of BMCU.
- The society/ milk collection centre insures the BMCU, provided the insurance coverage is available.
- The milk union/ dairy in coordination with the bank explores the possibility of getting subsidy under other schemes for purchase of BMCU by the societies/milk collection centres.
- The milk union/dairy can provided other services to the milk suppliers viz. supply of concentrate feed, fodder seed or rooted slips/ stem cuttings, veterinary and AI services, trainings, facilitate animal induction, etc.
- The union/ dairy provides tie-up arrangement for the repayment of bank loan out of sale proceeds.
- The union provides adequate compensation to the societies/ milk collection centre to meet the chilling cost of milk.
- The union/ dairy gives better price for good quality chilled milk supplied by the society/milk collection centre.

DPR for setting up BMC 1000 LPD
MODEL BANKABLE PROJECT ON BMC UNITS
PROJECT REPORT Of MILK PROCESSING (1000 LTR)
Compiled & Shared by- Team, LITD (Livestock Institute of Training & Development)
Image-Courtesy-Google
Reference-On Request.