Layer (Egg) Production Index : How to Calculate Egg Production in Layer Farms
PRODUCTION INDICES – LAYERS
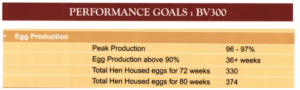
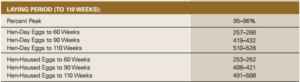
Egg Production
- Egg laying starts at 21stweek and the rate of laying (percentage production) increases every week to reach a level of 90% and above by 28 weeks of age which is maintained up to 40-42 weeks
- Afterwards, it slumps down slowly to reach 70% or below by 72 weeks of age. When the egg production goes below 65%, it is uneconomical to retain them unless the egg price is exceptionally high
- Egg production may be calculated as percentage on total number of birds available at 21stweek (hen-housed egg production) or on number of birds available on each day (hen day egg production)
Egg Production indices
Hen-day egg production percentage
- HDEP is mostly used for the scientific studies and truly reflects the production capacity of the available birds in the house.
- A farm average of 85% or more per year is desirable.
Hen-housed egg production percentage
- It is usually expressed in numbers. HHEP values of 80% or 295 or higher are desirable.
- Although HDEP is an excellent indicator of how well the live birds are laying, it does not consider egg size and egg quality.
- Since these factors help in determining the income from eggs, HDEP is often misleading from a profit standpoint.
- It also fails to account for past mortality. However, it is the best egg production index available and is universally used by the industry.
- From a cost of egg production standpoint, HHEP is good as it measures the effects of both egg production and mortality.
- If there is no mortality during a period, the HDEP and HHEP are equal.
Egg mass
- The use of egg mass rather than egg numbers will lead to better comparisons of flocks or strains of birds.
- To calculate egg mass it is first necessary to determine the average weight of eggs by weighing representative samples of the eggs produced.
Average egg mass = Per cent HDEP X Average egg weight in
grams (Per hen per day in grams)
Feed efficiency (Feed conversion ratio – FCR)
- Feed efficiency per kg egg mass
- This takes into consideration of the feed intake, egg weight and egg production. It is the ratio between the feed consumed and the egg mass.
FCR = Kg of feed consumed / Kg of egg produced
(per kg egg mass)
- A value of 2.2 or less is advantageous to the farm.
- Feed efficiency per dozen eggs
- This takes into consideration of the feed intake and egg production. It is the ratio between the feed consumed and the number of eggs produced.
FCR = (Kg of feed consumed x 12) / Total eggs produced
(per dozen eggs)
- A value of 1.5 or less is advantageous to the farm.
Egg feed price ration (EFPR)
- It is used to find out the ratio between the receipts from egg and expenditure on feed.
EFPR = Total value of egg produced / Total value of feed consumed
- An EFPR ratio of 1.4 and above is desirable.
You may have seen such production parameters in layer manuals. You may wonder what does it mean and how they can be calculated? Here in this article, we will see how these parameters can be calculated and what does it mean with examples.
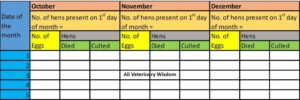
Record keeping chart should be formed as follows (en example)
- Total eggs per month
- Average eggs/bird/month
- Birds culled
- Birds died
The average egg production per bird can be calculated in three ways:
- Average egg production per bird per month(monthly average)
- Average egg production per bird on hen day basis(hen-day average)
- Average egg production per bird on hen housed basis. (Hen housed average).
Determining Monthly Average
The number of birds at the beginning of the month is added to the number of hens at the end of the month, and this total is divided by 2, to give an average number of hens for the month. Now a total number of eggs laid during the month is divided by the average number of hens for the month. This gives the monthly average production of eggs per hen:
Example: poultry farm has 5000 hens on first August 2016 and 4600 hens at the end of the month. The total, number of eggs produced were 96000. Find out the average egg production per hen during the month.
Calculations:
- Average number of hens of the month
= Number of birds at the beginning + Number of birds at the end / 2 = (5000+4600)/2 = 4800
- Average number of eggs per hen per month
= Total number of eggs laid/Average number of birds for the month = 96000/4800 = 20 eggs per hen per month
Hen Day Average (Average egg production on hen day basis)
A hen day average is obtained by dividing the number of eggs laid during a given period by the average number of birds on hand during the same period.
The hen-day average is usually determined on the monthly basis as follows:
(a) Total no. of hen day = Total no. of birds X No. of days in month
(b) Determine loss of days during the month due to culling or mortality of birds.
(c) % of egg production during the month = Total no. of eggs laid / Actual no. of hen days X 100
Example: A poultry farm contains 3000 hens of leghorn breed on the first of February 2008. If on 7th, 14th, 20th and 24th of the month 90, 120, 105 and 60 birds were culled, réspectively. The total egg production during the month was 60,000. Calculate the average egg production per bird on a monthly basis and hen-day basis. Also, determine the percentage of egg production on the farm.
Calculation:
Total No. of hen days = 28 (Feb.) X 3000 = 84,000
Loss of Hen days = (28-7) X 90+(28-14) X 120+(28-20) X 105+(28-24) X 60
= 21 X 90 + 14 X 120 + 8 X 105 + 4 X 60 = 4,650
- Actual no. of hens days = 84,000-4,650 = 79,350
No. of hens at the end of month = 3000 – (90+120+105+60) = 2625
Therefore, average no. of bird per month = 3000+2625/2 = 5625/2 = 2812.5 or say = 2813
Average egg production/bird on monthly basis = 60,000 eggs/2813 hens = 21.33
- Average No. of birds per month= (on hen-day basis)
= Actual number of Hen days/No. of days in the month = 79350/28=2834
- Average egg production per bird = 60,000/2834=21.17
Percent of egg production during the month = 60,000/79,350=0.7561 = 75.6%
Hen-Housed Average:
It Is obtained by dividing the total number of eggs produced during a given period by the number of birds in the flock at the beginning of the period. The hen housed average is usually obtained on a yearly basis. The total number of eggs laid during the last year is divided by the number of birds in the flock at the beginning of the Year. This method indicates income potential from a flock.
Example. A poultry farmer has 2000 white leghorn hens on the first of April 2015 on his farm, He culled 100 birds on 8th of the month and sold 160 birds on 15th April. His 190 hens died on 21st of this month and he culled 240 birds on 28th of the month. The total egg production during the month was 40,000. Calculate average egg production on Hen Housed basis.
Solution:
- Determining egg production on monthly basis:
No. of birds for the month in the beginning = 2000
No. of birds at the end of month = 2000 – (100+160+190+240) = 1310
Average no. of birds for the month 2000+1310/2 = 1655
So, average egg production per bird per month (monthly basis)
40,000/1,655 = 24.1692 eggs
- Determining total egg production on Hen-day basis
Total no. of Hen days should be = 2000 X 30 days = 60,000
Loss of “Hen-day” = (22 X 100)+ (15 X 160) + (9 X 190) + (2 X 240) = 6790
Therefore, actual no. of Hen-days = 60,000-6,790=53,210
Average no. birds birds for the month on Hen day basis
40,000/1,774 = 22.54 say 23 eggs
Percentage of egg production 40,000/53,210 X 100 = 75.1%
III. Total egg production on Hen- Housed basis = 40,000/2,000=20 eggs
CONCLUSION .
Lesser the need for culling from time to time in order to maintain egg production at an efficient level, and the lesser the mortaiìy during the year, the higher is the average egg production per bird and greater would be the profit.
Layer (Egg) Production Index
Compiled & Shared by- This paper is a compilation of groupwork provided by the Team, LITD (Livestock Institute of Training & Development)
Image-Courtesy-Google
Reference-On Request
.