Actinobacillosis
Actinobacillosis is a disease caused by ” Gram negative coccobacilli”.
What is coccibacilli?
It is type of bacteria having both rod and oval shape appearences as its name suggests too.Cocci are those bacteria which have oval shape and bacilli are those which have rod shape . If bacteria shows both morphologies it is called as “coccibacilli”.
₪Genus of Gram negative coccibacilli:
It belongs to the genus Actinobacillus.
Name of microorganism causing wooden tongue (Actinobacillosis):
A.lignieresii
Actinobacillus mostly target cattles,sheeps and very rarely affect pigs, dogs, and horses.
It attack causes the formation of granulomas filled with pus containing small,hard yellow to white granules.
Its target of infection changes when animal changes like in sheep it does not commonly affect tongue. It cause the formation of granules in skin, neck , jaw, and face.In case of rupture,these granules discharge yellow-green pus .Mostly sheep die due to starvation as they feel difficulty and pain in passing eatables from their throats.
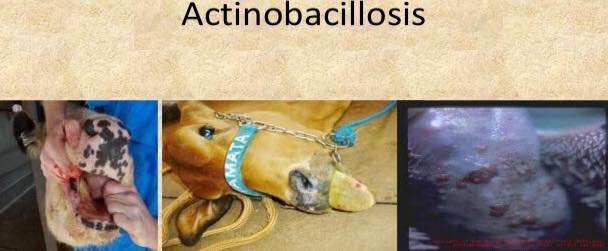
While in cattle , It mainly affects the tongue. That’s why. actinobacillosis is also called as wooden tongue. In cattle it less likely cause the formation of granules at sites like jaws, lungs, and skin.
Animals die due to starvation and thirst when the infection is at acute stage but as it reaches the chronic stage ,fibrous tissue gets deposited and the tongue becomes immobile and eating gets difficult or even impossible .
How to diagnose?
The diagnosis of this infectious disease can be done by microscopic examination of the smears made from pus,or by culturing the causative agent.
The microscopic examination of pus will show the colonies of gram negative coccibacilli. It is the best way to identify this infection.
From where this infectious organism enters into an animal body :
This organism attacks the soft tissues of the mouth. When an animal is given rough fodder (containing thorns , pointed bushes etc)it damages their soft tissue like epithelilal tissues.As a result,organism enters the tissues of the mouth through damaged epithelial.
Clinical signs :
.Affected animal will be inable to eat and drink.
.protruding tongue.
.formation of nodules, granules and ulcers visible on the tongue.
.drooling saliva.
Treatment :
1.Avoid feeding animals rough fodder as it can damage their mucosa (linning inside of the mouth containing stratified squamous epithelium).
2.Intravenous injections of sodium iodide (70mg/kg). Affected animal will show improvement in a very short time period after this injection.
Injection should be administered at least twice, 7-10 days apart.
.Administration of potassium iodide orally.
.Antibiotics can be used too like streptomycin , tetracycline and
tilmicosin.