Animal Trafficking and Illegal Trade: Consequences and Solutions
Mohima Langthasa, BVSc&AH Student, 3rd year
Lakhimpur college of veterinary science, Assam Agricultural University,787051
Abstract:
Animal trafficking, a clandestine industry driven by demand for exotic pets, traditional medicine, and luxury goods, poses significant threats to global biodiversity and animal welfare. This article explores the intricate network of illegal trade routes, highlighting the devastating consequences on vulnerable species and ecosystems. Through an analysis of enforcement challenges, socio-economic factors, and emerging trends, it elucidates the urgent need for coordinated international efforts to combat this illicit trade and safeguard the planet’s precious wildlife.
Introduction:
Illegal trade refers to the buying, selling, or exchange of goods, services, or commodities in violation of laws or regulations. It encompasses various activities such as smuggling, trafficking in drugs, weapons, wildlife, and counterfeit goods, among others. Illegal trade poses significant challenges to global security, economies, and the environment, often fueling organized crime, corruption, and instability. Efforts to combat illegal trade involve international cooperation, law enforcement initiatives, and public awareness campaigns.
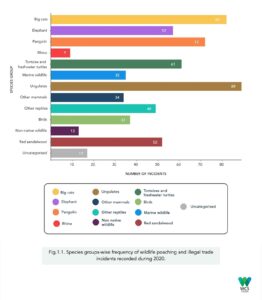
Incidences of animal trafficking in India:
- Assam: Rhino Horn Trafficking: Assam’s Kaziranga National Park has been a hotspot for rhino poaching due to the high demand for rhino horn in traditional medicine markets, particularly in East Asia.
- Operation Wildnet: In 2016, India’s Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) conducted Operation Wildnet, a nationwide crackdown on wildlife trafficking networks. This operation led to the arrest of numerous individuals involved in illegal wildlife trade, including the seizure of tiger skins, bones, and other wildlife products.
- Ivory Seizures in Kerala: In recent years, Kerala has seen several incidents of ivory smuggling. In one such incident, in 2018, authorities seized a large consignment of ivory tusks being smuggled from Africa.
- Turtle Trafficking in West Bengal: West Bengal has faced issues with the trafficking of freshwater turtles. In 2019, authorities intercepted a truck carrying hundreds of endangered turtles illegally destined for the pet trade.
- Leopard Skin Seizure in Maharashtra: Maharashtra has seen incidents of leopard skin smuggling. In 2020, forest officials seized a leopard skin and arrested individuals involved in its trafficking.
- Illegal Bird Trade in Delhi: Delhi has been a hub for the illegal bird trade. In 2017, authorities rescued hundreds of rare birds, including parakeets and mynas, from illegal traders in the city.
Causes of animal trafficking:
- Demand for exotic pets: People often desire rare or exotic animals as pets, driving a demand for species that are illegally captured and traded.
- Traditional medicine: Certain animal parts and products are used in traditional medicine, leading to the exploitation of wildlife populations.
- Status symbol: Owning exotic animals can be seen as a status symbol in some cultures, further driving the demand for illegal wildlife trade.
- Cultural practices: Some cultures have traditions or rituals that involve the use of animal parts, such as ivory or rhino horn, leading to poaching and trafficking of these animals.
- Profit motive: Wildlife trafficking can be highly profitable, with some species fetching high prices on the black market, incentivizing poachers and traffickers.
- Lack of law enforcement: Weak enforcement of wildlife protection laws and corruption can enable illegal traders to operate with impunity.
In impoverished communities, people may turn to poaching and wildlife trafficking as a means of earning income or supporting their families.
- Habitat destruction: Destruction of natural habitats due to factors such as deforestation and can displace wildlife, making them more vulnerable to trafficking.
- Conflict and instability: Regions experiencing conflict or political instability may have weakened law enforcement and oversight, facilitating wildlife trafficking.
- Lack of awareness: Many people may be unaware of the impact of wildlife trafficking on biodiversity and ecosystems, leading to a lack of public pressure to combat the trade.
Consequences of animal trafficking:
- Threatened Species: Many animals targeted for trafficking are already endangered or threatened. Illegal trade exacerbates their decline by removing individuals from already vulnerable populations.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Removing species from their natural habitats can disrupt ecosystems, leading to imbalances in predator-prey relationships, competition for resources, and changes in biodiversity.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Trafficking often targets species with unique ecological roles. Their disappearance can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, leading to reduced resilience to environmental changes.
- Spread of Diseases: Trafficked animals can carry diseases that may spread to humans and other species, posing public health risks. For example, the illegal trade of exotic pets has been linked to the spread of zoonotic diseases like monkeypox and avian influenza.
- Animal Cruelty: Many animals suffer during trafficking due to poor handling, confinement, and transportation conditions. This cruelty extends to the methods used to capture and kill animals, such as poaching and trapping.
- Disruption of Local Communities: Illegal wildlife trade often involves local communities who may rely on these resources for their livelihoods. However, it can also lead to exploitation, conflict, and corruption within these communities.
- Economic Impact: Wildlife trafficking undermines legal wildlife-based industries such as ecotourism and sustainable hunting, which contribute to local economies. It also deprives governments of potential revenue from regulated trade.
- Social Consequences: Participating in wildlife trafficking can have legal repercussions, including fines, imprisonment, and damage to reputations. Additionally, it can perpetuate social inequalities and corruption within societies.
Solutions to control animal trafficking:
- Legislation and Enforcement: Strengthening laws against wildlife trafficking and enforcing them rigorously can deter traffickers and buyers. This includes imposing severe penalties for offenders.
- International Cooperation: Collaborating with other countries to share intelligence, resources, and best practices can help in tracking and intercepting trafficking networks that operate across borders.
- Demand Reduction: Raising awareness about the consequences of wildlife trafficking and reducing demand for products derived from endangered species through education and advocacy campaigns.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities living near wildlife habitats in conservation efforts by providing alternative livelihoods and empowering them to protect their natural resources.
- Technology: Employing advanced technologies such as drones, GPS tracking, and DNA analysis to monitor wildlife populations, detect poaching activities, and apprehend traffickers.
- Capacity Building: Providing training and resources to law enforcement agencies, customs officials, and wildlife authorities to effectively combat wildlife crime.
- Criminal Justice System Reform: Improving the efficiency and transparency of the judicial system to ensure swift prosecution and conviction of wildlife traffickers.
- International Conventions and Treaties: Ratifying and implementing international agreements such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) to regulate and monitor the trade in endangered species.
Conclusion:
Animal trafficking and illegal trade are significant issues with far-reaching consequences. The exploitation of wildlife for profit not only threatens the survival of numerous species but also contributes to ecological imbalance and biodiversity loss. Additionally, these activities often involve cruelty and exploitation of animals, posing ethical concerns. It’s imperative for governments, organizations, and individuals to work together to combat this illicit trade through enforcement of laws, raising awareness, and supporting conservation efforts.
Acknowledgement:
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to Dr.Biju Borah, PhD Assistant Professor, Department of Veterinary & Animal Husbandry Extension Education, Lakhimpur College of Veterinary Science, for giving me this opportunity to study and write an article on the above topic.
References:
https://unity.edu/careers/how-to-stop-poaching/
https://images.app.goo.gl/nQUeNNUrvGqp1fiQ9
https://images.app.goo.gl/7CL1E31LtMMw586PA