APPLICATION OF ETHNOVETERINARY PRACTICES & VETERINARY HOMEOPATHY/ VETERINARY AYURVEDA IN TREATMENT OF MASTITIS IN DAIRY CATTLE
Dr. Deep Narayan Singh
Assistant Professor
Department of Livestock Production Management
College of Veterinary Science & Animal Husbandry
DUVASU, Mathura-281001
ABSTRACT
Ethno-Veterinary medicine is a holistic interdisciplinary study of the local knowledge about the importance & utilities of different parts of plants with animal health care and husbandry practices for optimizing productive & reproductive performances of livestock. Livestock industry provides a major source of livelihood for many people worldwide, particularly the rural poor and tribes in developing countries. The Indian subcontinent has rich in terms of ethno-veterinary health traditions. Several types of herbs, shrubs and plants have been used for treatment and prevention of various animal and human diseases. Hence, to keep animals healthy, traditional healing practices have been applied for centuries in our countries and have been passed down orally from generation to generation. Mastitis is one of the most significant diseases of dairy cattle especially higher yielder and it reduces the profit earn by the livestock owner. It is generally associated with infectious in origin resulting in an inflammatory reaction in the mammary gland of the cow. Several herbal extract & preparations for example turmeric, allovera, giloe, drumsticks, satawari etc along with homeopathic drugs like phytolacca, Calcaria, Tetasule and ayurvedic treatments can be used to treat the various stages of mastitis in dairy cattle to reduce the economical losses.
Key words: Aloe vera, Drumstick, Herbes, Ethno-Veterinary, Mastitis,
Introduction
Herbal medicinal plants are being used for the treatment of various human and livestock ailments by the local peoples since earliest times. It is a recognized fact that several herbs, shrubs and plants are an important source of ethno-veterinary medicines. Ethno-veterinary practices are more common in almost all developing and developed countries especially in India, China, Pakistan, Nepal, USSR, USA, Bhutan and Bangladesh etc. Herbal medicines serve as safer alternatives as growth promoters due to their suitability and preference, lower cost of production, easy to grow and cultivate, improved feed efficiency, fast growth and reduced mortality in dairy cattle. The various components of several herbs, shrubs and plants are used as medicines for treatment of many types of human and animal’s diseases. Herbal medicines comprise plant-based medicines can be used for therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic application in animal health care and disease prevention. Ethno-veterinary knowledge is acquired through practical experience and has traditionally been passed down orally from generation to generation. Various central & state Universities viz. Central Drug Research Institute (Lucknow), Anand Agricultural University (Gujarat), National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) and SABAR Dairy union of Gujarat state extensively propagate the ethno-veterinary concept by providing field training and motivating personnel involved in animal husbandry.
Cattle play a very important role in the human civilization and livelihood security since old days. Ethno-Veterinary practices concern to animal healthcare is as old as the domestication of various livestock species. The extract of various parts of plant has shown to exhibit antibacterial, antifungal, insecticidal and antioxidant activity. High producing lactating animals are very much susceptible with mastitis. It is the most common problem and costly disease of dairy cattle in all over the world. In mastitis, due to faulty milking practices invasion of bacteria through teat canal leads to inflammation of udder parenchyma and tissues. Mastitis affects both the quality and quantity of milk. Mastitis can be identified by abnormalities in the milk, alteration in milk pH, udder parenchyma with or without systemic illness. Big economic losses are mostly due to pathogen-mediated damage of milk secreting tissue of udder and subsequent reduced milk production of affected animals. Due to mastitis there is annual loss of Rs. 7165.51 Crore in India. In allopath, the mastitis treatment requires higher dosage of advanced antibiotics with at least 3-7 days leads to various side effects such as antibiotic residues and toxic metabolites in milk, meat and animal byproducts. Hence, in the rural areas of India, the traditional herbal, homeopathic and ayurvedic medicines are used by the local people for treating the mastitis.
Herbal therapy of Mastitis
- Application of paste of Turmeric powder and fresh leaves of Drumstick (Moringa oleifera) mixed with common salt over the infected udder of cattle & buffalo thrice in a day is very effective.
- Mixture of 200 g Aloe vera (200g), turmeric powder (50g) and lime (5g) paste was found to be suitable to treat all type of mastitis without any adverse effects. The treated animal recovered within 5day after treatment.
- Use of 50 g turmeric powder, 20-25 g limetone, 250 g Aloe vera and lemon juice of two fresh lemon, mix it thoroughly to make a paste150-200 ml of water and apply externally over the affected part of udder. Repeat 10 times a day up to 5 days.

- Feeding of 20-30 gm camphor in banana fruit twice in day up to three days is also very effective in milk with blood or abscess condition.
- Hot fomentation of udder by using neem leaves boiled in hot water with magsulf and boric acid and apply over teat thrice in a day.
- In severe mastitis condition (rooten of teat or udder) crushed the 100 gram leaves of sponge guard in 250 ml of water and applies over the affected part f teat or udder and tied with cotton cloth.
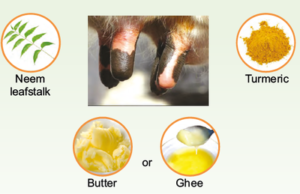
- In mild teat infection, freshly plucked & clean leaf stalk of neem leaves and making the paste of turmeric powder with butter or ghee and coat this paste over affected teat.
- Use of palm oil, medium chain fatty acids for treatment of mastitis, having the antibacterial properties.
- The extract of, Garlic (Allium sativum)and Black Cumin (Bunium persicum)is also used for treatment of mastitis.
- The used of garlic (Allium sativum)cloves are widely used for treating the mastitis.
- The antimicrobial activities of Ageratum conyzoides, Muntinga calabura, Piper betle, and Curcuma domestica have been proved in various research studies.
- Massaging with mentha oil is also useful for treating mastitis.
- The fine powder of white stone (Benachu kallu) mixed with desi butter. The whole blending process should be over Betel leaf (Piper betle). The mastitis infected udder should be cleaned with fresh warm water which contains turmeric powder and common salt mixture with equal amount. Thereafter the paste should apply over the mastitis affected inflammatory udder of cow or buffalo from top to bottom and left for drying about 20-30 minutes. Finally Sambrani (Benzoin resin) smoke used to fumigate the mastitis affected udder for 5 – 10 minutes for better recovery from mastitis.
- Prepare fine wood ash powder of non-poisonous wood used for cooking, by sieving. Mix the wood ash with half a litre of water and stir until a paste is formed. Tether the affected cow and milk the cow before treatment. Apply the paste on the udder of the cow and massage the affected area.
- The leaf paste of Trichodesma indicumis used to treat mastitis in cattle in Karnataka.
Homeopathic treatment of Mastitis
- Use of 5 drops of Phytolacca-1000 orally in morning hours up to 15 days can be cured from mastitis.
- In case of fibrosis and nodules formation in secretary tissues we can use Homeopathic drugs Tetasule fibrokit gold, Tetasule Fibro, Fibro-K drops for such purposes.
- 2ml of Calcaria Flour-200C in 100 ml of Luke warm water is administered orally thrice a day to each animal. Silicea -200C is also administered in same dose and route keeping a time gap of half an hour between two administrations. The treatment is carried out for at least 20 days.
- Belladonna 30 or 200 and Urticaria urens 30, when udder is hot, painful and edematous.
- Conium 200, when udder is very hard with yellowish and cheesy milk
- Various homeopathic drugs are available in the market among which Tetasule, Masti-K drops and Mastitis drops are very effective in mastitis of cattle.
Ayurvedic Treatment of Mastitis
As per the texts of Ayurveda, mastitis is known as Sthanavidhradi, a disease of pitta origin, the drugs used in this formulation (Aloe vera, Curcuma longa and Calcium hydroxide) means three ingredients viz. Gheekumari (Aloe vera) 2 or 3 petal, Haldi (Turmeric) powder (50gm) and Chunna (Lime stone)- 10 gm is potent pitta shamaka (Pacifies Pitta humour). The formulation possesses Krimighna (antimicrobial), Vranashodaka (wound cleanser), Vranaropaka (wound healing), Shothahara (anti-inflammatory) and Srotoshodaka (channel cleanser) properties. Hence, mastitis can be efficiently managed with this formulation by application of such paste at least for 7-10 days. Sometimes oral administration of 50 gm of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) with two lemon juice dissolved in 200 ml of water is also effective in treating the mastitis during early stage.
Conclusion:
The excessive, exhaustive and indiscriminate use of higher antibiotics for treatment of mastitis with steroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs leads to a lot of side defects along with their residual effect in the milk, meat and other animal products and byproduct as well as there may be development of antibiotic resistance. Health hazards issues will be created by use of hard and prolong antibiotic treatments for mastitis. Hence, for treating the animal diseases like mastitis, ethno-veterinary medicine, homeopathic and ayurvedic treatment is now safer and better alternatives for human and animal health concerned. There is a great need to start the awareness programme about the collection, dispersal of traditional knowledge and compilation of facts about the ethno-veterinary practices by the villagers. Government of India should also taken necessary initiatives to promote the ethno-veterinary practices and starts a course curriculum by implementation of degree or diploma course to enrich the knowledge and conduction of research about the ethno-veterinary practices along with homeopathic and ayurvedic treatments for mastitis and other animal diseases.
REFERENCES
https://www.rroij.com/open-access/ethnoveterinary-formulation-for-treatment-of-bovine-mastitis-.pdf
- Agarwal T, Singh R, Shukla AD, Waris I, and Gujrati A. (2013). Comparative analysis of antibacterial activity of four Piper betle Advanced Applied Science Research. 3: 698–705.
- Ameen F, Reda SA, El-Shatoury SA, Riad EM, and Enany ME. (2019). Prevalence of antibiotic resistant mastitis pathogens in dairy cows in Egypt and potential biological control agents produced from plant endophytic actinobacteria. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 26(7): 1492-1498.
- Grzesiak, B., Kołodziej, B., Głowacka, A. and Krukowski, H. (2018). The Effect of Some Natural Essential Oils Against Bovine Mastitis Caused by Prototheca zopfiiIsolates In Vitro. 183(3):541-550.
- Harjanti D, Ciptaningtyas R. and Wahyono F. (2019). Phytochemical properties and antibacterial activity of Ageratum conyzoides, Piper betle, Muntinga calaburaand Curcuma domestica against mastitis bacteria isolates. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 247:012049.
- Krishna, L., Swarup, D and Patra, R.C. (2005). An overview of prospects of ethno-veterinary medicine in India. Indian. J. Anim. Sci., 75: 1481-1491.
- Rajeswari T, Venugopal A, Viswanathan C, Kishmu L, Venil CK, and Sasikumar JM. (2010). Antibacterial activity of honey against Staphylococcus aureusfrom infected wounds. 1:537–541.
- Sri Balaji, N. and Vikrama Chakravarthi, P. (2010). Ethnoveterinary practices in India – A Review. Vet. World., 3: 549-551.
- Thangadurai R, Venilla M, and Shanmugam P. (2017). Management of Mastitis in Dairy Cattle using Herbal Combination. Journal of Krishi Vigyan. 5(2):164.
- vikaspedia.in. Ethenoveterinary practices in animal care.



