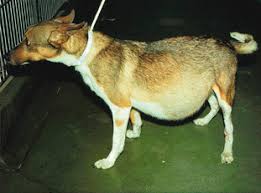
ASCITIES IN ANIMALS
Definition—Accumulation of excess (>25 ml) peritoneal fluid( Lymphatic fluid between two layers of peritoneum) in the abdominal cavity caused by impairment of mainly Liver and also accompanied by impairment of Heat & Kidney indicating abdominal dissention. Human may survives maximum 5 years but animals 1 year depending upon degree of Ascities. Normal peritoneal fluid prevents friction between outer /parietal layer & inner/visceral layer of peritoneum. Ascities may develop within hours to weeks.
- Aetiology—
1-Liver Origin–
- Liver Cirrhosis (scarring) cause 80% chance of Ascities.Hypertensin of Portal Vein result leaks of fluid from blood to peritoneum.
- Non alcoholic fatty liver
- Hepatitis-B & C
- Auto immune hepatitis
- Genetic Liver Disease( homochromatosis,wilson’s disease,alpha-1-anti trypsin deficiency
- Icterus( Jaundice) for obstruction/rupture of Billiary duct, CBD( common Bile Duct),,
2-Cardiac origin-
- Congestive Heart Failure( CHF) of Right & Left
- Jugular vein dissention & increase jugular pulsation
- Cardiac murmur or arythimea in case of Rt. CHF
- “Muffled heart sound” indicating Pericardial effusion & tamponade( compression of heart)
3-Nephral origin–
- Kidney failure of hepato-renal syndrome
- Urethral / Ureter Obstruction
4-Miscelanious-
- Cancer of abdominal organs
- Infections – spontaneous infection called “spontaneous bacterial peritonitis(SBP)”
- Lungs- Specifically Rt .Lung filled with Gases or fluid
- Lymphoadenopathy-adenoma of Lymph Glands
- Symptoms-
- Pear shaped abdominal distension with rib impression, abdominal pain,
- Swelling of joints of lower extremities( ankle)
- Shortness of breath during even mild exercise ,Staircase riding etc. due to accumulation of fluid in Right Lung & hypoxia resulting even throacentesis.
- Digestive problems-bloating( tympani),abdominal pain,indigestion,constipation,decrease appetite
- Back pain as abdomen is descended resulting increase curvature of Spinal chord
- Difficulty in Laying /sitting
- Fatigue & exercise intolerance
- Hernia of Umbilical or Inguinal due to abdominal pressure
- Fever indicative of inflammatory disorder
- Hyponatremea indicating increased thirst, impaired free water excretion
- Hypokalemea indicating decreased renal distal tubular filtration having normal adrenal function.
- Patho- physiology of Ascities–
- Peritoneum is constitute of two layers. The inner layer/visceral layer is constitute of serous membrane of mesenchymal cells & connective tissue but external layer/parietal layer is consists of transversalis fascia of abdominal wall. Peritoneal fluid prevents frictional erosion between above to layers. This lymph mainly come from exchange of solutes & fluid of Diaphragmatic Lymphatic vessels & maintain a define volume. Accumulation of peritoneal fluid for alteration in forces governing fluid exchange across the membrane, increased portal hydrostatic pressure due to obstruction of venous flow, hypoalbumuninemea , decrease colloidal plasma pressure , increased permeability of capillaries due to infection, decreased lymphatic uptake for reduced lymph flow , redistribution of plasma fluid is affected due to cardiac impairment affecting RAS( Renin-Angio-Stenin) system resulting accumulation of Na & H2O effecting more lymph production than excretion. RAS also cause splanchnic arteriolar Vaso dilation for Nitric Oxide retention. Liver impairment for congestion of venous of hepatic portal vein compression/obstruction also cause Rt.CHF .Rt. CHF causing ascities is more common in Dogs as increase portal pressure for obstruction of caudal vena cava by thrombosis/diaphragmatic hernia, hepatic lymph contains more protein than intestinal. Renal impairment for decreased GFR( Glomerular Filtration Rate), loss of albumin( protein).Onchigenic growths cause inflammation & obstruction of capillaries resulting more lymph retention. Infections of mainly bacterial enhances Neutrophil resulting obstruction of capillaries with increased permeability, Trauma resulting rupture of capillaries resulting bleeding & accumulation of fluid.
- Diagnosis-
- USG(Ultra Sono Graphy)- Cranial displacement of Diaphragm for hepatomegally, peritoneal fluid accumulation, organic echogenic tissue response, neoplasm,hepatic lipidosis, more peritoneal fluid status, Ultra sound guided peritoneal fluid aspiration through a 22 gauze hypodermic needle for biopsy or different tests.
- Commuted Tomography( CT Scan)
- Radiography—organomagally, mass lesion, effusion , Diaphragmatic hernia, other hernia, pericardial effusin,aortic displacement etc.
- FNAC(Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology) for cancerous growth / organomagally
- Laboratory tests like Creatinin, cholesterol, triglyceride, Bilirubin level, cytological evaluation etc.
- PCV( Packed Cell Volume) (>10%)if aspirated peritoneal fluid is sanguineous & compared with peripheral blood.
- Blood collected from intra abdominal viscera contains platelets so blood clot is formed but previous bleeding blood does not contain no platelets so no blood clot.(DD)
- The aspirated fluid is to be under C/S ( Culture & Sentivity ) test for bacterial isolation & sensitive Anti biotic
- In human albumin gradient of ascities fluid with normal serum is guide line but in animals carries less importance.
- CBC( Complete Blood Count),serum Biochemistry schedule, Urine analysis(R/M-Routine & Microscopic).
- USG guided Renal biopsy for glomerulonephropathies.
- USG guided Lymph Node biopsy for assessing LN function indicating congestion of veins & cytology.
- Dirofilaria test as Heart Worm cause cardiac. LN. Pulmonary hypertension
- Echo-Cardiograph( ECHO) & Electro-Cardiograph(ECG) (eCG- Equine Gonadotropin hormone)
- Thoracic radiograph for pulmonary metastasis of oncogenic cells, Rt.CHF,
- Abdominal visceral Tuberculosis complications
- ‘Slippery “ feeling on palpation of small bowel in normal case & “fluid wave” feeling in ascities.
- Paracentesis- Extirpation/extraction/drain of excess peritoneal fluid from abdomen for relieve abdominal dissention/ ultra sound guided blood aspiration from Liver, Spleen etc or small effusion aspiration for Laboratory tests
- Administer Local Anaesthesia9optional but usually not necessary in Animals),sterilise the scheduled puncture site with aseptic lotion, aspirate with 22 gauze hypodermic needle attached to 10-20 ml syringe of Nylon/glass with penetration on needle at slightly caudal to ventral mid line of Abdominal wall below naval point to avoid puncture of intra abdominal visceras like Liver, Spleen, Urinary Bladder, Pancreas, GIT etc under standing posture or on lateral recumbency of Animal.
- Suction of peritoneal fluid through a needle to reduce the peritoneal fluid as well as for Laboratory test like cancer/infection/portal hypertension/other conditions
- Transudate from Paracentesis-the effusion contains low to moderate Cells present(1000-7000 Cells/microlitre), low protein concentration(<2.5 gm%) ,chyle( milky fluid formed from Fat to be released from Lymph Glands of small intestine to enter into Lymphatic system) is present moderately indicates
- Exudates from Paracentesis-High Cellular(>7,000 cells/micro litre) & High protein(2.5 gm%)) indicates
- The aspirated peritoneal fluid is to be preserved under EDTA( Ethyl Diamine Tetra acetic Acid)
- Smear of fluid is to be made immediately .
- The smear is to be on a cytospin slide( centrifuged content is deposited in a circular manner on a slide as smear of monolayer cells)
- Contraindications of Paracentesis-( complications)-
- Lacerated of Liver. Spleen, tumour, neoplasm as may aggravate the condition
- Chance of extension of infection to intra abdominal visceras
- Peritoneal fluid infection
- Treatment- Absolutely no complete cure from Ascities but palliative treatment advised for comfortable longer life..
- Limiting (2000-4000 mg/day)sodium consumption ( Na Cl-Table salt as in Ascities Na level increase.
- Diuretics( ex-furosemide-lasix @ 1mg/kg/PO or I/M or I/V bidor spironlactone-aldactone-@ 1mg/kg/PO/twice daily)
- Paracentesis- May be practised weekly basis or as per requirement
- TIPS( Trans jugular Intrahepatic protosystemic Shunt)- A wire mesh( stent) is introduced to portal vein to inflate for forming a canal(shunt) to bypass the Liver
- Liver Transplant in Liver Cirrhosis case
- If for abdominal wall weakness or thinness them meshing with stainless steel wire mesh/plastic mesh/otherwise
- Surgical manipulation in caseof neoplasm
- AB for infection
- Colloidal therapy (Plasma,albumin,Hetastarch,pentastarch etc) in case of hypoalbuminemia(lack of adequate albumin production by body system).
- Prevention-
- Balanced diet
- Regular deworming including filarial medications ( in D/C for Dirofilariasis)
- Limit table salt intake
- Regular exercise
- Regular weight check & monitoring ( if > 4 kg ain alternate day)
- Avoid excess NSAID( Non-Steroidal Antinflamatory Drugs) like aspirin, ibuprofen etc as hamper renal function
- Low Salt diet with 2-4 gm of Table salt per Day & Low salt food specifically low Potassium( K) containing fruit/food ( as seeds of fruit/vegetables contain more ‘K’.
Differential Diagnosis-
- Obesity– Truncal symmetric Obesity for Hypothyroidism
- Physiological Pregnancy- Mating Date & Oestrus Date
- Distended Urinary Bladder- Urine Infection /Cancer of UB
- Gastric dilation (obstipation)- Obstruction of strangulation, intususpension, torsion of SI etc. Obstipation is common in Cat with mega colon.
- Hepatomegally for venous congestion due to Rt.CHF/Hyperadenocorticosim or Spleenomagally for venous congestion due to spleen rotation—FNAC /USG/CT
- Peritonitis –High Cellular & High protein in Paracentesis exudates. (ex-Feline septic/non septic peritonitis) cause abdominal pain.
- Pancreatitis—Oily. white stool
- Idiopathic compact cell mass development in Organs( Organomagally for Lymphosracoma/neoplasm/etc — USG/CT
Prepared & presented by Dr.Keshaba Chandra Samantaray ,M. V. Sc. (Gynaecology), Gold Medallist, OUAT, Bhubaneswar, NET(ICAR-New Delhi),”Bioinformatics in Optimising Fertility in Farm Animals”- College of Veterinary Science -PAU(Ludhiana),”Caprine AI { Goat Artificial Insemination }”—MGSRD Institute, Phalton, Maharastra, “Gender Awareness & Integration in Traing Curiculla”-Institute of Rural Management( IRM) Anand,Gujurat.”Livestock & Environment Interactio”-Internatinal Agricultural Centre( IAC),Wageningen,The Netherlands.”Talks on“Go-Bandhya Nirakaran”+”Mai Jersy Bacchurira Jatna”+Garvini Gaira Jatna”-All India Radio,Cuttack. Acceptance of my suggestions on Constitutional Reforms of Republic of India”. “Project Management Skills”-MANAGE, Hyderabad (including Classes on Inter Personal Relationship {IPR} at National Police Academy, Hyderabad. Ex-JD, FSB, Chiplima, Sambalpur.