Cultured Meat: Pioneering a Sustainable and Ethical Food Revolution
Dr. Iqra Arif* and Brindha S.*
*PhD Scholar
Department of Veterinary Public Health and Epidemiolgy
College of Veterinary Sciences, GADVASU, Ludhiana
Introduction
In recent years, the global demand for meat has surged alongside population growth and rising affluence. However, traditional animal agriculture has been associated with numerous challenges, including environmental degradation, animal welfare concerns, and inefficiencies in resource usage. To address these issues, scientists and innovators have turned to a groundbreaking solution: cultured meat. This article explores the concept of cultured meat, its production process, potential benefits, and the implications for the future of food.
What is Cultured Meat?
Cultured meat, also known as lab-grown meat, in-vitro meat, or clean meat, is a product derived from animal cells that are grown in a laboratory setting. The process involves isolating cells from living animals, such as cows, pigs, or chickens, and cultivating them in a nutrient-rich medium. Over time, these cells multiply and differentiate into various tissue types, eventually forming muscle fibres, fat cells, and other components that make up meat.
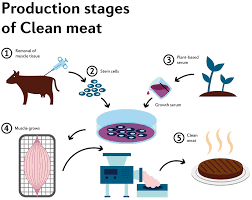
The Production Process
The production of cultured meat begins with a small sample of animal cells obtained via a harmless biopsy. These cells are then placed in a nutrient-rich medium that provides the necessary elements for cell growth and multiplication. The medium contains a combination of carbohydrates, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals to support cell development. To promote tissue formation, scientists employ bioreactors, which are large-scale vessels that provide a controlled environment for cell growth. Within the bioreactor, the cells receive oxygen and are periodically stretched or exercised to enhance their texture and mimic the natural muscle structure found in conventional meat.
Benefits of Cultured Meat
- Sustainability: Cultured meat has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with traditional livestock farming. It requires fewer natural resources, such as land, water, and feed, and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions. This sustainable aspect could help mitigate climate change and alleviate pressure on land and water resources.
- Animal Welfare: Cultured meat production eliminates the need for raising and slaughtering animals for food. By reducing or eliminating animal suffering, it offers a more humane alternative to conventional meat production.
- Food Security: With the world population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, meeting the growing demand for meat will be a challenge. Cultured meat offers a potential solution by providing a resource-efficient and scalable method of meat production that can meet future protein needs.
- Health and Safety: Cultured meat can be produced in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of contamination by foodborne pathogens and reducing the need for antibiotics or hormones often used in traditional animal farming. Additionally, it allows for customizing nutritional content, potentially creating healthier meat products.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the concept of cultured meat holds great promise, several challenges remain. The production process is currently expensive and requires further refinement to achieve cost-effectiveness and scale. Additionally, regulatory frameworks need to be established to ensure safety and transparency in the emerging cultured meat industry. Nevertheless, the progress in cultured meat research and development has been remarkable. Several companies have already conducted successful taste tests and are working towards commercialization. As production methods improve and costs decrease, cultured meat has the potential to become a viable and widespread alternative to conventionally produced meat.
Conclusion: Cultured meat represents a groundbreaking innovation in the food industry, addressing sustainability, animal welfare, and food security concerns. As technology advances and the industry continues to evolve, cultured meat has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume meat, offering a more ethical and sustainable future for our planet and its inhabitants.
References:
- Gaydhane, M. K., Mahanta, U., Sharma, C. S., Khandelwal, M., & Ramakrishna, S. (2018). Cultured meat: state of the art and future. Biomanufacturing Reviews, 3, 1-10.
- Pandurangan M, Kim DH (2015) A novel approach for in vitro meat production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi. org/10.1007/s00253-015-6671-5
- Sharma S, Thind SS, Kaur A (2015) In vitro meat production system: why and how? J Food Sci Technol 52:7599–7607. https ://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1972-3
- Bonny SPF, Gardner GE, Pethick DW, Hocquette J (2015) What is artifcial meat and what does it mean for the future of the meat industry? J Integr Agric 14:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/ S2095-3119(14)60888-1
- Kumar P, Chatli MK, Mehta N et al (2014) Meat analogues: health promising sustainable meat substitutes. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2014.939739