Deepa Saini and Beena Pathak
Department of Food Science and Technology, GB Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Pantnagar, Uttarakhand (263145)
Introduction:
Foods nowadays are not only meant to relieve hunger and provide the requisite nutrients for humans, but also to avoid nutrition-related illnesses and enhance consumers’ physical and mental health. To strengthen public health, dietary authorities and associated organizations have regularly urged a reduction in the intake of foods associated to the prevalence of chronic diseases, and increased consumption of fruits and vegetables, grains, legumes, low-fat dairy products, lean meats and seafood, especially fatty fish species rich in n-3 PUFA. According to the persistence of these guidelines, there is a significant degree of knowledge in the people and, fortunately, nutritional composition is already a major factor in the choice of foods by the consumer.
However, the need for nutritious food is high, but customers are hesitant to change their dietary habits. So this necessitates modifying the composition and converted the food in such a form or ingredients that are beneficial to health of consumer, and egg have this capability due to presence of bunch of nutrients and functional properties. Eggs are a nutritious inclusion in the diet for people of all ages and at different stages of life. In fact, eggs can play an incredibly useful role in diets of those at risk of low nutritional intakes, such as elderly people, pregnant women and children. So it will not be erroneous if we call it “nutrient goldmine”.
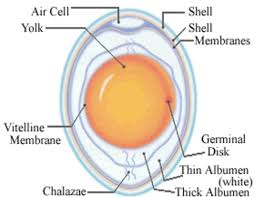
Fig 1: Structure of egg
Nutritional composition of egg:
The complexity of eggs allows them to have a range of functions in food while also providing nutrients necessary for finest health. With calories, egg provides daily nutrients required by the body such as protein, riboflavin, biotin, iodine, selenium and choline. Eggs also provide vitamin D, vitamin A, folate, phosphorous, omega-3 fats, and the antioxidants, lutein and zeaxanthin. Egg protein is a high quality protein since it contains essential amino acids. There is also scientific evidence that eggs contain other biologically active compounds that may have a role in the therapy and prevention of chronic and infectious diseases. The presence of compounds with antimicrobial, immunomodulator, antioxidant, anti-cancer or anti-hypertensive properties have been reported in eggs. Additionally, eggs are an important source of lecithin and are one of the few food sources that contain high concentrations of choline.
However, as a component of egg lecithin, choline has numerous important physiologic functions and it is a required nutrient that is essential for the normal development of the brain. Eggs also supply omega-3 fatty acids, mainly in the form of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). DHA helps maintain brain function and vision. Owing to their high nutritional value, eggs are also an important food that should be included in the planning of diets for patients, and are especially
valuable in feeding people with gout, because it is a source of protein that does not add purines. Additionally, for people in sports training, egg proteins may have a profound effect on the training results, because, by its inclusion in the diet, it could be possible to enhance skeletal muscles synthesis.
Table 1: Nutritional composition of egg per 100 g
| Component (Unit) | Amount | Component (Unit) | Amount |
| Egg shell (%) | 10.5 | Calcium (mg) | 56.0 |
| Egg yolk (%) | 31 | Magnesium (mg) | 12.0 |
| Egg white (%) | 58.5 | Iron (mg) | 2.1 |
| Water (g) | 74.5 | Phosphorus (μg) | 180.0 |
| Energy (Kcal) | 162 | Zinc (mg) | 1.44 |
| Protein (g) | 12.1 | Thiamine (mg) | 0.09 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 0.68 | Riboflavin (mg) | 0.3 |
| Lipids (g) | 12.1 | Niacin (mg) | 0.1 |
| Saturated fatty acids (g) | 3.3 | Folic acid (μg) | 65.0 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids (g) | 4.9 | Cyanocobalamin (μg) | 66.0 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids (g) | 1.8 | Pyridoxine (mg) | 0.12 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 410 | Retinol equivalents (μg) | 227.0 |
| Iodine (μg) | 12.7 | Potassium (mg) | 147 |
| Tocopherols (μg) | 1.93 | Carotenoids (μg) | 10 |
| Selenium (μg) | 10 | Cholecalciferol (μg) | 1.8 |
| Egg shell (%) | 10.5 | Calcium (mg) | 56.0 |
Apart from nutritional properties egg is known for functional properties like foaming ability, emulsifying, thickening, binding, leavening properties which makes it a versatile ingredient for food industries to make value added products.
Egg-consumption advantages to ensure both physical and mental health of humans:
Eggs contain several vitamins and minerals that are essential parts of a healthful diet. So it play vital role in several body functioning as follows:
- Energy production: Egg provides energy as it comprises of all the nutrients required for generation of energy and also build and repair body tissues and cells.
Healthy brain: Egg contains lecithin and choline. Adequate choline intake is associated with better memory and learning abilities.it is also necessary for the nervous system to
- function effectively. Choline is used to make acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter that influences memory.
- Strong muscles: The protein in eggs helps maintain and repair body tissues, including muscle
- Healthy eyes: Presence of carotenoids maintains eye-sight and best known for their function in the neural retina. Carotinoids also have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions, and thereby, is considered to play a role reducing immune-mediated macular degeneration and age-related cataract formation. Other vitamins in eggs also promote good vision.
- A healthy immune system: The vitamin A, vitamin B-12, and selenium in eggs are key to keeping the immune system healthy.
- Healthy skin: Some vitamins and minerals in eggs help promote healthy skin and prevent the breakdown of body tissues. It was researched that egg-yolk phosvitin has the potential to be used as a natural bioactive compound as a hyper-pigmentation inhibitor for human skin. A strong immune system also helps a person look and feel well.
- Weight loss and maintenance: The protein in eggs can help people feel full for longer. This can reduce the urge to snack and lower a person’s overall calorie intake.
- Healthy hairs and nails: Fat, protein, iron, and vitamins promote hair growth and prevent hair fall.
- Healthy heart: Eating egg does not increase cholesterol and help to prevent strokes and heart attack.
- Healthy pregnancy: Nutrients like folic acid, iron, calcium, vitamins and minerals are required by pregnant women and this requirement fulfilled by eggs including other food items in diet. It also helps to prevent congenital disabilities, such as spina bifida.
- Reduce risk of breast cancer: Consumption of egg in daily diet can reduce the risk of developing breast cancer due to presence of significant amount of choline i.e. needed for normal functioning of cells.
To experience the health benefits of eggs, a person should eat them as part of a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grain, milk etc. Along with healthy diet physical activities, sports, games, yoga, meditation is also important to maintain good health.