FACTS AND BENEFITS OF CONSUMING CHICKEN EGG
Udaykumar, Siddharth Savale, Dhanraj Girimal, Vidyasagar, Gurunath pasare, Shivkumar kamthane, Satishchandra biradar.
Veterinary College, Bidar, Karnataka.
Introduction:
Chicken rearing practices was probably started before 7500 BC. Eggs have been valuable foodstuffs since from many years. The most commonly used bird eggs are chicken, duck, and quail eggs. Chicken egg is a main component of the human diet serving as a dietary source of protein, fat, and other nutrients and it is considered as food with high bioavailability. Egg has all nutrient component which is required by human health it play significant roles in health of eyes, cardio metabolic related risk, for pregnant women and children. Egg protein serve as reference protein for defining the quality of other proteins. As per ICMR one person should consume at least half egg per day to meet the protein requirement.
Nutrient composition of eggs.
Eggs provides different nutrient such as fat and water soluble vitamins like vitamin A, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, vitamin B12 and choline. It is also a rich source of minerals like phosphorus, zinc, iron and magnesium. However, the diet of laying hens and cooking method also may affect the nutritional quality of eggs. Nowadays chicken eggs that are especially high in omega-3 fatty acids are produced by feeding hens a diet containing polyunsaturated fats from sources such as fish oil, chia seeds, or flaxseeds which are known as designer eggs.
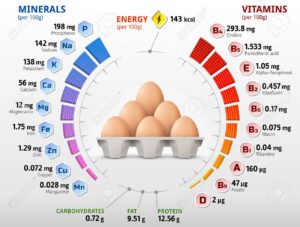
Physical composition of egg of various species:
| Chicken | Quail | Turkey | Duck | |
| Egg weight(g) | 57 | 12 | 85 | 80 |
| Yolk (%) | 30 | 32 | 32 | 35 |
| Albumen (%) | 60 | 48 | 56 | 53 |
| Shell (%) | 10 | 20 | 12 | 12 |
Chemical Composition:
| Components
(100%) |
Whole egg | White
(56-60%) |
Yolk
(27-32%) |
Shell and Shell Membrane |
| Water | 65.0 | 87.0 | 48.0 | 2.0 |
| Protein | 12.0 | 11.0 | 17.5 | 4.5 |
| Fat | 11.0 | 0.2 | 32.5 | – |
| Carbohydrate | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | – |
| Ash | 11.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 93.5 |
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Role of eggs in human health:
- Improves mental health: Egg is a rich source of choline which is required for neurotransmitter synthesis. The ICMR recommends the addition of choline to prenatal vitamins because of its essentiality in promoting cognitive development of the offspring.
- Role in Vision: Lutein and zeaxanthin reduces the risk of developing cataracts and slow the progression of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts. Lutein and zeaxanthin also act as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions. (Miranda et.al. 2015)
- Other uses:
- Phosvitin has a high potential to be used as an anticancer agent for humans .
- Lysozyme has also been found as the ability to enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy treatments. Therefore, this protein is becoming a promising co-adjuvant therapy against cancer (Hernandez, Ledesma & Hsieh, 2017).
- Cystatin from hen egg white exhibits a very broad spectrum of effects, e.g. antimicrobial and anticarcinogenic.
Myths and Facts of consuming egg:
| Myths | Facts |
| Brown eggs are healthier than white eggs | No substantive nutritional difference between Brown eggs and white eggs. |
| Free range and cage free eggs have more nutritional values. | Nutritional content of eggs is determined by hens diet. |
| Fertile eggs have less or no cholesterol | No substantive nutritional difference between fertile and infertile eggs. |
| Egg is Non-vegetarian | Table eggs are infertile |
| Consumption of egg will increase the cholesterol in body | A single medium-sized egg contains 186 mg of cholesterol, which is 62% of the recommended daily intake |
| Cooking of egg will destroys the protein content of egg. | Raw egg has anti nutritional factor called avidin which binds with biotin and prevents it from being absorbed, but if the egg is cooked, it denatures avidin and biotin is easily absorbed by your body. The egg will still contain of protein after the egg is cooked; only the structure of the protein will change |
* As per Egg Nutrition Center (ENC) of American Egg Board (AEB)
Conclusion: Eating habit has more influence on health of person. This can be achieved by consumption of eggs. This will meet all the nutrient requirement thus helps in improving physical and mental health of person.
REFERENCE:
- Jose M. Miranda, Xaquin Anton, Celia Redondo-Valbuena, Paula Roca Saavedra, Jose A. Rodriguez, Alexandre Lamas, Carlos M. Franco and Alberto Ceped. Egg and Egg-Derived Foods: Effects on Human Health and use as functional food. Nutrient
- Hernandez, Ledesma & Hsieh. 2017. Chemopreventive role of food-derived proteins and peptides: A review. Food science and Nutrition.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi.
- Egg Nutrition Center (ENC) of of the American Egg Board (AEB)



