FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE IN DOMESTIC ANIMALS WITH ZOONOTIC IMPORTANCE
Foot and mouth disease is also known as Aphthous Fever a contagious viral disease of all cloven footed animals characterized by presence of vesicles in oral mucosa and foot. It is economically important disease, because it spreads very fastly affecting large animal population which affects global trade and it causes heavy mortality and production losses.
Etiology: Aphthovirus belonging to picornaviridae family which is non-enveloped ss RNA virus. It epitheliotropic virus. Seven different antigenic types/ serotype are A, O, C, Asia-1 SAT-1, SAT-2, SAT-3. Symptoms and lesions produced by each serotype are similar but do not give cross protection. In India, only four types A, O, C, Asia-1 are prevalent, out of which type O is predominant followed by Asia-1, A and C type. SAT-1, SAT-2 and SAT-3 are prevalent in South African Territories.
Host: it affects all the cloven footed animals – cattle, buffaloe, sheep, goat, pigs mostly, including wild ruminant (deer, antelop), giraffe, bison boar, yalk etc. It is fatal in young animals and rarely fatal in adults.
Transmission :Virus is voided in saliva, semen, milk and urine. Infection occurs by ingestion of contaminated feed and water. Aerogenous or droplet infection occurs when mucous membrane of URT is affected.Virus is also transmitted by humans and animal. Incubation period is few hours to few days.
Pathogenesis:
Infection occurs by ingestion of contaminated feed and water. Virus reaches to gastric or intestinal mucosa where it invades the epithelial cell, multiply and produces focal areas of degeneration and inflammation. From here, it invade lymph and enters to blood circulation and reaches to the epithelium of other mucous membrane and skin. The most favorable cell for multiplication of virus is middle layer of stratum spinosum. These cells undergo liquefactive necrosis and the cells over these foci, undergoes hydropic degeneration forming micro-vesicles. Micro-vesicles fuse together forming large vesicles. The roof of vesicle is made up of stratum corneum, stratum lucidum and stratum granulosum. Base is composed of stratum germinatum. These lesion are also occurs in the epithelium where squammous epithelium is present viz, tongue, buccal mucosa, rumen, reticulum, omasum, skin of teats, cleft of foot and coronary bands.
Symptoms :
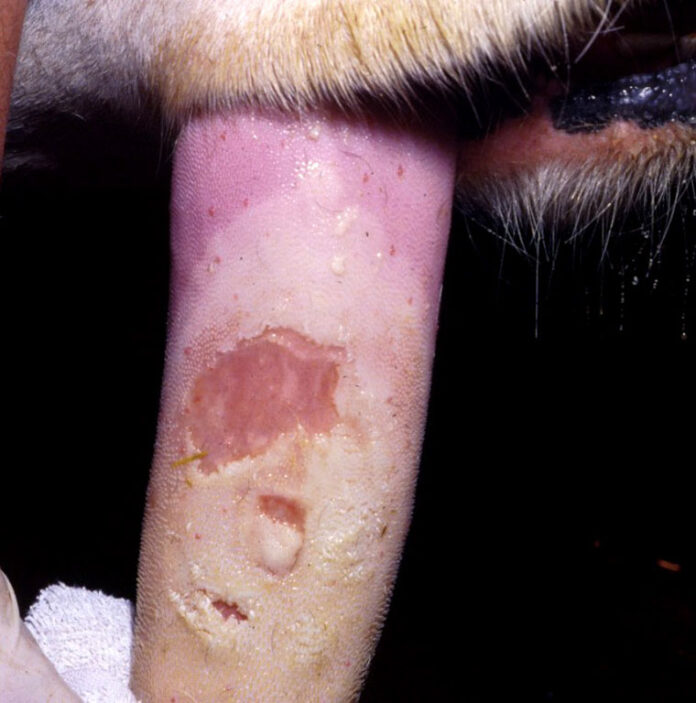
Fever (102-104°F) and sudden fall in milk yield in cattle is observed. Animal shows excessive salivation and make eating painful. The saliva hangs in long, ropy stringes. Smacking of lip and tongue is characteristic. Vesicles appears on buccal mucosa, dental pad, tongue and coronate of feet which ruptures leaving raw painful surface. Lameness due to vesicles on cleft and coronates of feet. Vesicles also occurs on teats, vulva and conjunctiva. When teat orifices involved, severe mastitis occurs. Abortion and infertility are common squeal. In young calve, heavy mortality due to mayocardial necrosis occurs. In cattle, due damage of endocrine by FMD, a chronic syndrome of dyspnoea, anaemia, overgrowth of hair and lack of heat tolerance is observed which is called as “Panting”. And such cattle are called as Panters.
Gross lesions
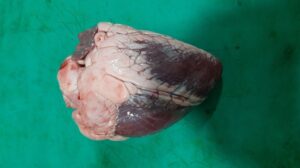
Presence of vesicles in mouth cavity (buccal mucosa, dental pad, lips, palate, tongue), cleft or coronate of feet, teats of mammary glands, udder, vulva, rumen, reticulum, omasum, skin of brisket, dewlap, perineum region etc., which may rupture producing the ulcers. Severe mastitis occurs in adult animals. In young animals, (calves, lambs young pig or goats), in the wall and septum of left ventricle of heart, grayish necrotic foci of irregular size is observed which give the myocardium a striped appearance hence called as “tiger heart” or “tigroid heart”. Gastroenteritis is also seen young animals.
Microscopic lesions
Hydropic degeneration in stratum spinosum cells of epidermis leading to formation micro vesicles. The roof of vesicle is made up of stratum corneum, stratum lucidum and stratum granulosum. Base is composed of stratum germinatum. The vesicle contains necrotic epithelial cells leucocytes and occasional erythrocytes.
Heart: Microscopically, hyaline degeneration and necrosis of muscle fiber alongwith intense lymphocytic infiltration is seen in heart. Gastroenteritis characterized by haemorrhgaes and oedema.
Zoonotic importance
Natural infection may occurs in humans. However, in humans, the diseaseis usually mild and limited to acute fever associated with appearance of vesicles on the hands, feet, and oral mucosa.
Diagnosis
Symptoms and lesions, Immunodiagnostic tests for demonstration of antigen/ antibody – CFT,ELISA. Isolation of virus and its typing and Electronmicroscopy
Dr Sourabh babu and Dr Vivek Kumar
Division of pathology, ICAR-IVRI