by -Dr Deependra singh Shekhawat.
R.M, Stellapp Tech.Pvt.Ltd.
Hoof affections are second largest cause for economic loss in livestock farming . In India, the incidence of foot disorders is 8-10% in Dairy cattle . The over grown hooves is the most common predisposing condition of the hooves that accounts for more than half of the total foot lesions. I get a lot of hoof affections and my recent interest was on preventive management of hoof affections in dairy cattle.In our area particularly in urban area where dairy cattle are kept on hard concrete floor, such problems are quite prevalent. Through this starting segment of Bovine lameness series my attempt will be to give some insights on common hoof ailments and their surgical management. Bovine lameness is a SILENT KILLER and huge production loss entity in any organised dairy farming. Pain induced reduction in milk yield is a much focused area for dairy scientist ans Dairy vets .
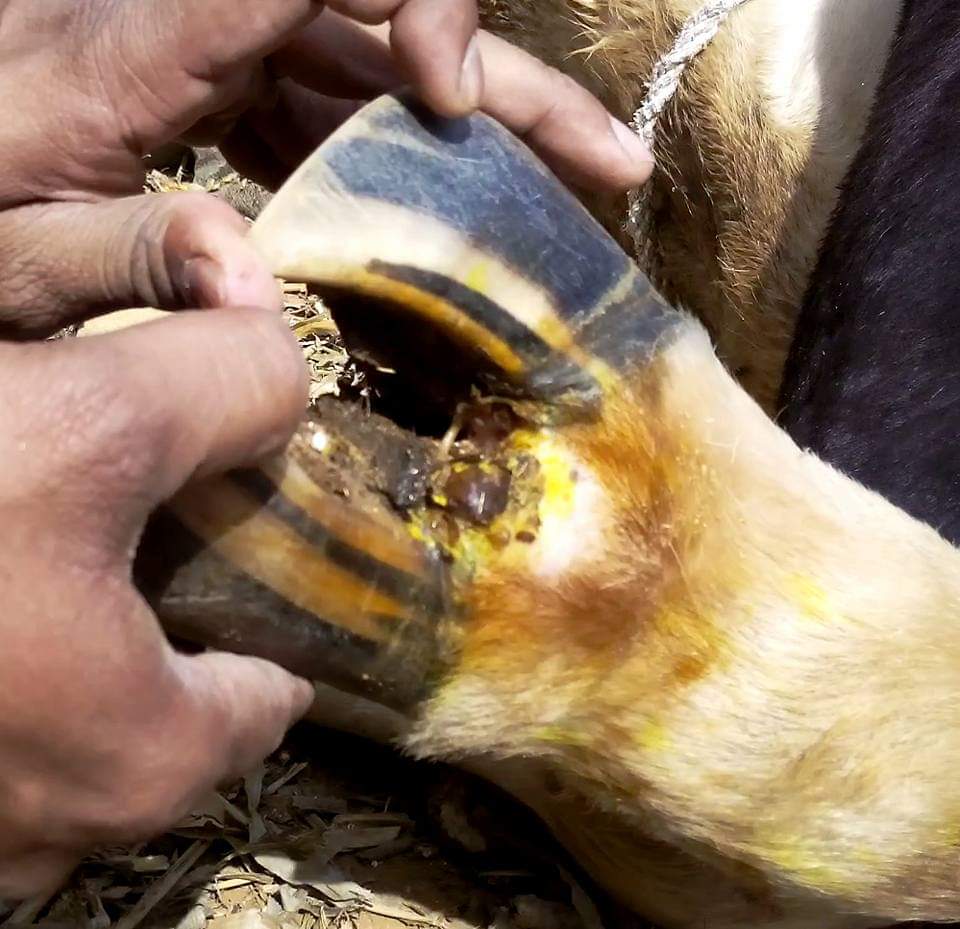
Interdigital fibroma also termed as Interdigital hyperplasia or corns are firm fibrous masses consisting of hyperkeratotic and parakeratotic skin found in the interdigital space of cattle
The lesions appear as secondary to chronic skin irritation due to environmental, conformational and hereditary factors. Where lesions become large and/or infected, surgical removal is the preferred treatment. Improved hygiene and appropriate hoof trimming are the keys to prevention of this condition
“Cork screw claw” is the over grown claw with inward curvature making the inter digital space widened. This is a genetic disorder and this predisposes to many inter-digital affections in cow. Dairy cows tend to have a higher prevalance of interdigital fibromas in the rear feet, probably owing to the rear feet contacting more moisture from manure and urine than the front feet. Cork screw claw is generally seen in front limb and due to this reason secondary inter-digital fibroma is common sequelae to cork screw claw in bovines

Surgical management of interdigital fibroma :-
For surgery, animals are best positioned in chemical restraint. Xylazine Butorphanol and Ketamine combinations proves to be excellent in my experience. A tourniquet should be placed above the fetlock to provide hemostasis.Intravenous regional perfusion or local interdigital injection of a local anesthetic agent should provide adequate surgical anesthesia of the area.Sharp dissection should be accomplished, being certain to remove all proliferated tissue,including tissue immediately adjacent to the coronary band.Care should be taken to avoid damage to the coronary band.
Levlling of the curved claws can be done using an electric hoof trimmer and the inter digital wiring can be done after making fine hole of 3 mm diameter using electric drill.An orthopedic stainless steel wire can be used The toes can be wired together to decrease movement of the claws, but this may not be necessary in housed animals.The entire foot, including the solar surface should be incorporated in a tape bandage with or without gauze. Systemic antibiotics may be indicated if the fibroma is infected.
In some cases even cauterization of the growth can be done followed by antiseptic dressing with povidone iodine or bismuth iodoform paraffin paste. The antiseptic dressing should be continued for a minimum period of 3 to 4 weeks. The animal should be kept on dry floor.Following surgery, the animal should be kept in a dry area for approximately 2 weeks.
Preventive management:-
• Timely hoof trimming that prevents the widened inter-digital space resulting from over grown hoof and exercise is the best preventive management practices for this condition.
• Ensure that cattle stall is made of firm dry floorings. Proper drainage is a must to avoid water logging resulting in the hoof affections in the cattle.
• Weekly checking the hoof of the animal and cleaning the hoof with 1% potassium permanganate solution can check the spreading of hoof infections.
• Interdigital hyperplasia caused by poor conformation is very likely to recur, since the predisposing conformation problems will usually remain after removal of the growth.
• Animals suspected of having interdigital hyperplasia due to hereditary factors should not be used for breeding
Reference-On request.