Manure as a breeding material for flies and fly borne disease
Authors- Narender Kumar Poonia (teaching associate at livestock research station, Kodemdesar, RAJUVAS, Bikaner)
Garima Choudhary (teaching associate at livestock research station, Kodemdesar, RAJUVAS, Bikaner)
Article
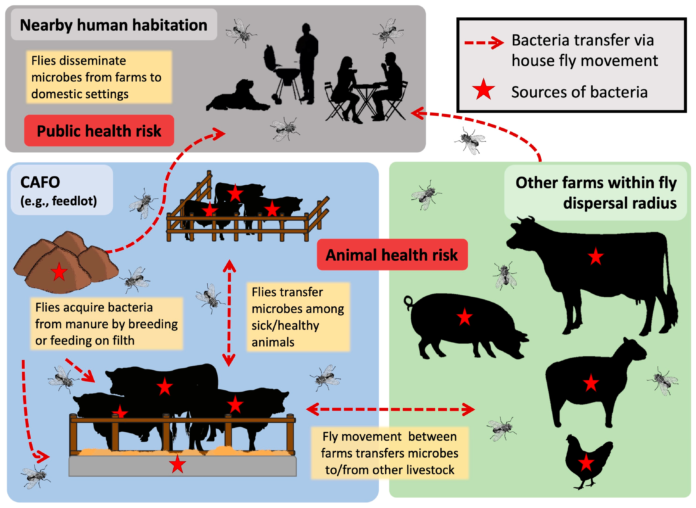
There are a number of flies which use the manure as their breeding material like musca domestica (common house fly), musca sorbens, fannia canicularis, musca stabulans and stomoxys calcitrans (stable fly). The excreta of horse and pig and cattle dung are the most favoured materials for these flies to breed. House flies lay their eggs in dark places in small masses of 120 to 150 under the surface of manure. The eggs develop into larval stage which after hatching may migrate from dung covering 2-3 feet distance and burrow in soli upto 4’’ and develop to pupa stage. These flies complete their life cycle under optimum temperature and moisture in 2 to 3 weeks. The stomoxys fly deposit its eggs in the moist, decaying vegetable matter such as piles of waste litter and farm yard waste and satle farm yard manure mixed with straw. The biting flies like haematobia may also be found in dung lying on pasture.
Fly borne disease
- Dysentery, Cholera, Typhoid fever
- They act as carriers of cornybacterium pyogens which causes summer mastitis in dry cows and heifers.
- Housefly carries Anthrax spores and parasitic worms.
Method of manure Disposal to prevent Fly Breeding
http://ecoursesonline.iasri.res.in/mod/page/view.php?id=74351