MYCOTOXINS & MYCOTOXICOSIS: A HEALTH HAZARD
Compiled & Edited by-Dr. Rk Singh
A mycotoxin from Greek word ‘mykes’ meaning fungus and “toxin” meaning poison. Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by organism of fungi kingdom commonly known as molds. They can grow on variety of different crops and foodstuff including cereals, nuts, dried fruits, apple, juice, coffee often under warm and humid condition.300-400 known species of mycotoxin. Mycotoxin group of naturally occurring chemicals produced by certain mold (Aspergillus)
The term’ mycotoxin’ usually reserved for the toxic chemicals products produced by fungi like Aspergillus and Fusarium that readily colonize crops.one mold species may produce many different mycotoxin and the same mycotoxin may be produced by several species.
Mycotoxicosis
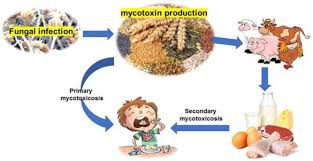
Mycotoxicosis is disease caused by natural toxin produce by fungus. Mycotoxicosis is term used for poisoning associated with exposures to mycotoxins.the symptoms of mycotoxicosis depend on type of mycotoxin. The concentration and length of exposure as well as age, sex of exposed individual .the synergetic effects associated with several other factors such as genetics, diet and interactions with other toxin have been poorly studied. Therefore, it is possible that vitamin deficiency, caloric deprivation, alcohol abuse and infectious disease. Status can all have compound effects with mycotoxin .mycotoxin have potential for both acute and chronic health effects via Ingestion, skin contact and inhalation. These toxic enter the blood and lymphatic system .They inhibit the protein synthesis and damage macrophage system. Inhibit the the particle clearance of the lung and increase sensitivity to bacterial endotoxin.
Route of exposure
Eating food and drink containing toxin
Dermal absorption
Breathing moldy air in damp door areas
In animal food
There have been outbreaks of dog food containing aflatoxin in North America late 2005 /early 2006 and again 2011.
Mycotoxin in animal fodder particularly silage can decrease the performance of farm animal and potentially kill them .several mycotoxin reduce milk yield when ingestion by dairy cattle .high level of mycotoxin lead to the neurological problems and in some cases death. Prolong exposure particularly harmful. Four most common genera of indoor molds are cladosporium, pencillium, aspergillus and alternaria.
Symptoms
Skin rash
Nasal
Cough
Runny nose
Sinus
Congestion
Respiratory problem like wheezing
Chest tightness
Itchy eyes
Lethargy
Headache
Tachycardia
Depression
Condition linked to mycotoxin exposure
Aflatoxicosis (afflation)
Food poisoning, vomiting (vomit ion)
Cancer (afflation)
Birth defects (fumonisins)
Acute pulmonary hemorrhage
Aplastic anaemia (bone marrow)
Failure and bleeding (tricothecenes)
Categories of mycotoxins
Aflatoxin (aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin B2, aflatoxinM1,aflatoxin G1 and aflatoxin G2).
Monocerin psilocybin
Cytochalasin D
Phalloidin
Amatoxin
Fusarium sporotrichioides
Molds that have been known to potentially produce these toxin are:
Acremonium
Aspergillus
Stachybotrys
Penicillium
Chaetomium
Even though molds may potentially produce mycotoxin like
Fusaric acid
Pencillinic acid
Penitrem
Citrinin
Fusariocin
Transmission of Aflatioxins to Humans & Toxicity and biological effects of mycotoxin in foods
Aflatoxin in food commodities of20 parts per billion (ppb) and the maximum level for aflatoxin in milk products is 0.5 ppb.aflatoxin is a potent human carcinogen.it is a naturally occurring toxic metabolites produced by certain fungi (aspergillus flavus), a mold found on food products such as corn, peanuts, peanut butter .it act as a potent liver carcinogen in rodents and presumably, humans. Aflatoxin B1 and M1 determine in milk. Cow fed contaminated rations containing the mold metabolite aflatoxin B1 secrete low level of aflatoxin B1 and its metabolites M1 in milk. The relationship of aflatoxin between aflatoxin B1 intake by cows and excretion of afflation M1 I milk. ELISA and HPLC test performed for the detection.
Reference-On request.