Pig Post-Mortem Procedure for Sample collection
A post-mortem examination, also known as an autopsy, is the examination of a body after death. The aim of a post-mortem is to determine the cause of death.
To collect relevant samples for the early diagnosis of disease.
Equipment required
- standard post-mortem kit including boning and skinning knives, scissors, scalpel blades, forceps .
- large shears to cut through ribs and jaw, bone saw.
- shears or small axe and hammer for brain removal.
- personal protection equipment for vet.– overalls, gloves, mask, eye protection
- materials for sample collection — dry swabs, swabs in media (viral transport media), specimen jars for individual
- fresh samples, 10% formalin, large containers for pooled formalin fixed samples
- gel packs ,permanent markers for marking the samples and sample submission form etc.
Postmortem includes two parts
- External examination of body of pig
- Internal examination of different body organs
- Examine the animal for skin lesions, lesions on the eyes or ears, discharges from any orifice, evidence of diarrhea, swollen joints or traumatic injuries (i.e. tail bite injuries).
Sample skin lesions by collecting pieces of affected skin into a sterile container and into formalin.
Eyes and ears can be submitted whole in formalin for histopathology if they are abnormal.
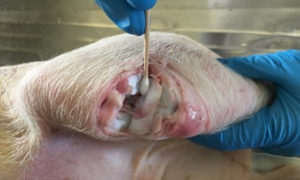
- In cases of lameness or joint swelling, open and sample the affected joints and a selection of major joints (i.e. hip joints, carpal joints, tarsus, stifle, and elbow).
Open the joint to take sample
Incise through the skin with a knife. Incise the joint capsule with a sterile scalpel and collect a sterile swab of joint fluid into sterile swab tube having PBS solution in it.
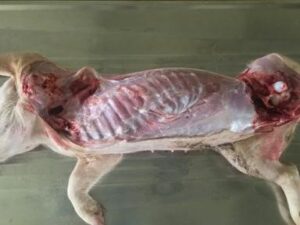
How to open a dead pig for postmortem
- Position the pig right side down. …lateral
- Open the abdomen and reflect the abdominal wall towards you; take care not to perforate the intestines. …
- Use shears to remove the rib cage by cutting along the bottom and top of the ribs. …
- Skin underneath the neck and chin.
Position the pig right side down. Reflect both limbs and skin the flank. Examine the musculature and hip joint.
Separation of skin ,fat and muscular layer
Open the abdomen and reflect the abdominal wall towards you; take care not to perforate the intestines. Look for peritoneal exudate; if present, sample into a sterile sample pot .
Separation of muscular layer of abdomen
Use shears to remove the rib cage by cutting along the bottom and top of the ribs. Trim away the diaphragm and muscle to expose the thoracic cavity.
Examine the organs in-situ. Record any abnormalities by writing a description and taking photographs. Collect any pleural or pericardial exudate into a sterile container or swab
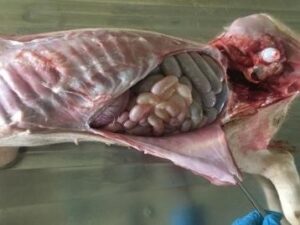
Abdominal organs
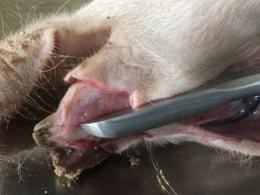
Skin underneath the neck and chin. Use shears to cut through the mandibular symphysis and split the lower jaw.
Lower jaw
Roll the head dorsally, split the lower jaw apart. Grasp and pull the tongue backwards while cutting the soft tissues along both mandibles.
Oral cavity
Examine the oral cavity. If there are oral lesions present (i.e. vesicles, ulcers) collect a sample into formalin, swabs .
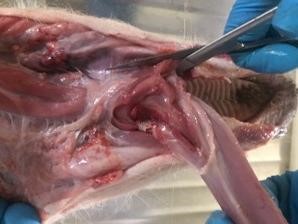
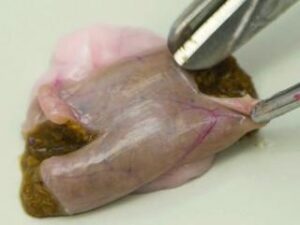
Tonsil
Sample the tonsils. The tonsils are the pitted, textured area of the soft palate outlined below. Using scissors, remove the tonsils. Place half into formalin and half into a sterile container.
Lungs
Bread slice the lungs to ensure lesions deep in the lung are not missed.
Collect thin sections (no greater than 1cm thick) of lung, trachea, bronchial lymph node, esophagus and any lesions into formalin.
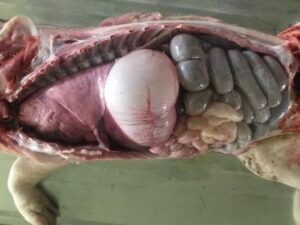
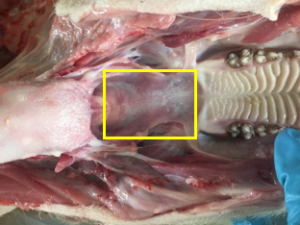
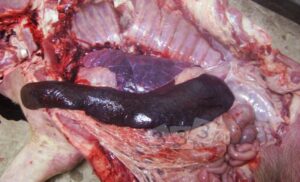
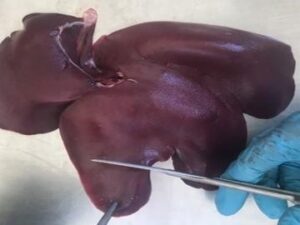
Spleen enlargement in ASF
In the abdomen, examine the spleen. Collect a 3cm cube of spleen into a sterile container and a thin section (<1cm) into formalin.
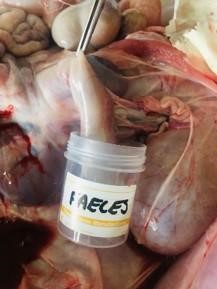
Cut the diaphragm away from the body wall. Grasp the mesenteric root and pull the viscera caudally, lifting the intestines and liver out of the abdomen and cutting the mesentery. The kidneys and urogenital tract should remain in the abdomen. Leaving the colon as the last point of attachment, incise the colon as far caudally as possible and collect a fecal sample.
Small intestine
Dissect the liver from the intestines. Examine and bread slice the organ. Collect a 3x3cm fresh sample of liver into a sterile container and a <1cm thick section into formalin.
Liver
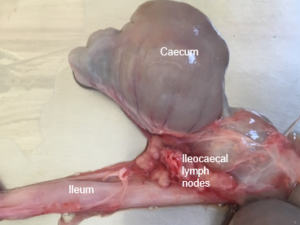
Spread out the intestine by cutting through the mesenteric root. Identify the ileum, caecum and ileocaecal junction .
Collect a 5cm long section of ileum and place half into formalin and half into a sterile container. Collect an ileocaecal lymph node into both formalin and a sterile container.
Ileocaecal junction
Examine the remaining sections of the intestinal tract. Open the stomach and examine the mucosa. Collect a sample of stomach contents into a sterile container and a piece of stomach into formalin. Examine the small and large intestine. Open sections of all areas of the intestinal tract and examine the mucosa, especially in cases of diarrhea.
Large intestine
Examine both kidneys:–Remove both kidneys, cut in half lengthways and examine the cortex, medulla and pelvis. Collect a 3x3cm piece of kidney into a sterile container. Collect a thin piece of kidney which includes cortex, medulla and pelvis into formalin.
Examine the bladder. If there is evidence of urogenital disease, collect a sample of bladder into formalin and a urine sample into a sterile container. Examine the urogenital tract (ovaries and uterus or testes).
All samples should be labeled clearly. Samples should be submitted as described in the sampling guidelines with a completed submission form.