by-DR. RAJESH KUMAR SINGH, (LIVESTOCK & POULTRY CONSULTANT), JAMSHEDPUR, JHARKHAND,INDIA 9431309542, rajeshsinghvet@gmail.com
The role of different variants of beta-casein on human health is a matter of concern worldwide. The status of A1/A2 beta-casein variants in Bos taurus cattle breeds from different countries has shown presence of A1 allele in European cattle. The data of beta-casein variant in zebu/Indian/ is not much more Bos Indicus available, however, a fewer investigations indicate presence of mostly A2 allele in Bos indicus that is safer for the health. Hence, we can conclude that the milk of our native cows and buffaloes is far safer than the milk of European breeds. The European breeds of cattle, particularly Holstein and Jersey are extensively used for cross breeding of Indian non-descript breeds. The presence of AI Beta-casein variant in Holstein and Jersey milk has been a matter of discussion since last couple of years over the use of these breeds in Indian crossbreeding programme.
Milk constitutes about 85% water, 15% milk sugar lactose, protein, fat, and minerals. Bovine milk is the most important food for young calves and a common source of proteins and microelements. In milk, there are two major protein groups known as caseins and whey proteins. Caseins account for 80% of bovine milk protein (Niki et al.1994; Martien et al. 1994), whereas, major whey proteins constitute about 14% (McLachlan 2001; Roginski 2003). Beta-casein is 30% of the total protein content in cow’s milk. Bovine milk contains 4 caseins: alpha s1 (CSN1S1, 39–46% of total caseins), alpha s2 (CSN1S2, 8–11%), beta (CSN2, 25–35%), and kappa (CSN3, 8–15%) (Eigel et al. 1984; Roginski 2003). There is also gamma-casein that is a product of degradation of beta-casein (Ostersen et al. 1997; Miller et al. 1990). Each cow carries two copies of the gene encoding beta-casein, with a genotype of A1/A1, A1/A2, or A2/A2. Neither the A1 nor A2 trait appears to be dominant (co-dominant), which means that the milk produced by an A1/A2 cow will likely to contain equal proportions of A1 and A2 beta casein. A1/A1 cows will obviously produce A1 beta-casein, just as A2/A2 cows will only produce A2 beta-casein. Caseins are encoded by members of a multigene family. The genes encoding 4 caseins are found on bovine chromosome 6 (Rijnkels 2002). The present article describes the beta-casein gene and the potential influence of beta-casein variants on human health.
Beta-casein polymorphism ——-
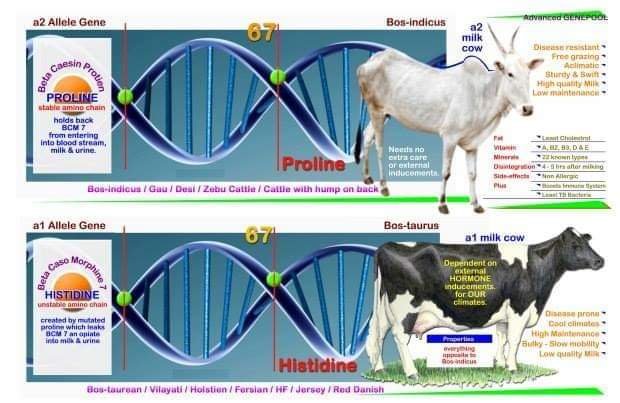
There are 13 genetic variants of beta-casein: A1, A2, A3, A4, B, C, D, E, F, H1, H2, I and G. The most common forms of beta-casein in dairy cattle breeds are A1 and A2, while B is less common, and A3 and C are rare (Farrell et al. 2004). Presence of proline (CCT) and histidine (CAT) amino acid in peptide chain at position 67 of the beta-casein may give rise to two variants A2 and A1 beta-casein respectively (Roginski 2003). The cause for concern with milk containing A1 beta-casein is that histidine at the 67th amino acid position allows a digestive enzyme to cut out a 7 amino acid segment of the protein immediately adjacent to that histidine.
However, proline is present in that location in A2 beta-casein, that same segment is either not separated at all or the separation occurs at a very low rate. The 7 amino acid segment that is separated from A1 beta casein is known as betacasomorphin-7, often abbreviated as BCM-7 (Kostyra et al., 2004).
Effect of BCM-7 on human health ————
The A1 beta-casein protein derived BCM-7 can affect many opioid receptors in the endocrine, nervous and immune system. Infants are having more chance of absorption of BCM-7 through their comparatively immature gastro-intestinal tract than the adults who are having a chance of showing local reaction in the intestine. BCM -7 is also considered to be an oxidant of Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) which may have some role in formation of arterial plaque. It is reported that BCM-7 may function as an immunosuppressant and impair tolerance to dietary antigens in the gut immune system which may contribute to the onset of Type 1 diabetes. BCM-7 has been implicated as a potential etiological factor in Type 1 diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, arteriosclerosis, sudden infant death Syndrome and also related with some neurological conditions such as autism or schizophrenia. A2 beta-casein has not been implicated for these conditions (Pattanayak, 2013). As a result the A2 Corporation was setup in New Zealand during 1990s to genotype cattle and market the milk with A2 beta-casein at premium price.
Prevalence of A1 and A2 allele in bovine————
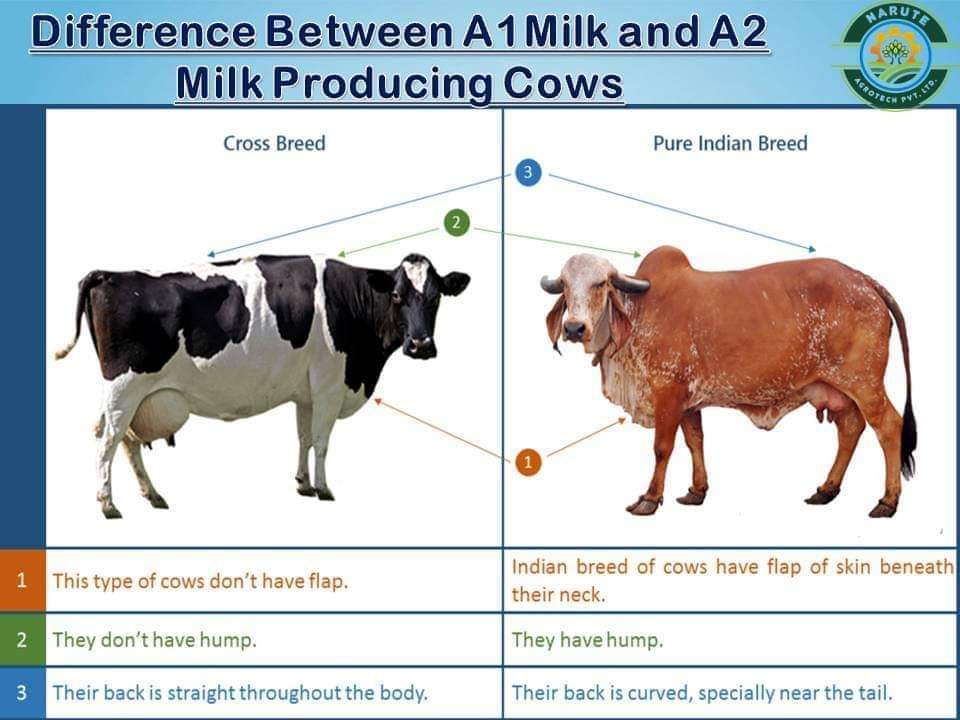
A2 beta-casein is found in most of the Western, African and Indian cattle and water buffaloes. A1 beta-casein is carried only by the cows of European breeds especially Holstein (Bos taurus) . Jersey has an A2 allele frequency somewhat higher than Holstein. But some Jersey cows carry one ‘B’ beta-casein allele which can release BCM-7 far more (Pattanayak, 2013). Beta-casein allele frequency in indigenous Indian cattle (Bos indicus) and buffalo breeds reported to have 99 to 100% presence of the A2 /A2 genotype (Mishra et al., 2009) and A1 /A1 genotype is absent among them as mentioned in table- 2 and 3. So, most of the indigenous cattle and buffalo breeds are homozygous for the A2 betacasein allele and good for health.
Reference:On request.