Revolutionizing Livestock Farming with Artificial Intelligence: Sustainable Transformations and breakthrough in Animal Welfare
Dr. Rutik Namdev Pawar1* and Dr. Sanjay Kumar Bharti2
1MVSc Scholar, Department of Livestock Products Technology, College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, DUVASU Mathura (281001), India
2Assistant Professor, Department of Livestock Products Technology, College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, DUVASU Mathura (281001), India
Abstract
The rapid advancement in artificial intelligence (AI) and sensor technologies have opened up new possibilities across various sectors, including livestock farming, which is often overlooked in traditional discussions. Artificial intelligence offers farmers exceptional support by minimizing resource use enhancing sustainability of feeding practices and increasing overall farm productivity. It helps reduce the carbon footprint and improves efficiency while lowering the likelihood of human error, making it a valuable tool for boosting farm productivity and sustainability. The key is the integration of cutting technology with human expertise. While AI and sensors provide real time, comprehensive, and objective insights, it is the farmer’s deep understaning of their livestock and environment that should guide the application of these technologies. Internet Of Things (IoT) and AI represent some of the most efficient and effective methods for modernizing livestock farming, playing crucial roles in managing farm operations, handling fields, and conducting research to improve production outcomes. This article explores how AI and sensor innovations can significantly enhance animal welfare in livestock farming causing on a human-centric approach.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Livestock Farming, Susainability, Animal welfare
Introduction:
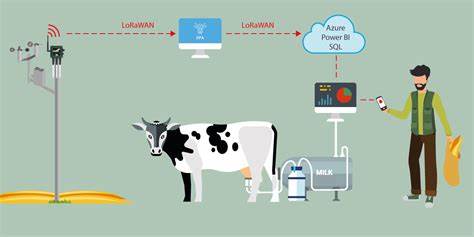
Artificial Intelligence and computer vision have transformed livestock management, these technologies enable automated animal identification using computer vision and RFID/QR codes, providing instant access to detailed records. Artificial Intelligence system monitor health, track growth and analyze feeding and reproductive behaviors, allowing early detection of issues and effective breeding management. Automation reduces labor and provides real-time insights, improving animal welfare and farm productivity. Artificial Intelligence process this data to provide insights that improve farming practices. By identifying the animal, the system can analyze the relationship between its weight and history, it streamlines quality assurance processes. AI can monitor animal health and welfare sound, activity patterns, feeding and water intake, radio frequency identification, and other precision livestock farming technology.
Artificial Intelligence processes this data, enabling farmers to detect these anomalies. Additionally, farmers can use the data to understand the relationship between specific foods and the weight and health of their livestock, making it a critical quality control tool.
Application of of Artificial Intelligence in Livestock Farming
Computer vision and machine learning algorithms can detect, categorize, and link these factors to specific health issue, automatically raising alerts when necessary. Technologies like cow movement analysis enhance livestock farming by identifying behavior and activity, monitoring feed intake, and tracking rumination.
Monitoring Drinking and Feeding Habits: Internet of Things devices with computer vision record livestock drinking and feeding patterns, providing farmers with valuable information. Sensors track consumption levels and rates both day and night, helping identify unusual eating habits that may signal behavioural or health issues. These patterns are vital for efficient quality control, as factors like daily activity levels, movement, and posture are significant indicators of animal health.
Monitoring Heat Stress: Sensors in AI-based systems collect temperature data, analyze its fluctuations, and link these changes to specific actions or behaviors. Machine learning models recognize patterns that increase the risk of heat exhaustion and send real-time alerts when temperatures reach dangerous levels.
Monitoring and Adjusting Conditions for Aquaculture and Sheds: Similar to animal excrement, livestock vocalizations provide important information, machine learning algorithms trained on audio recordings can detect and categorize anomalies in vocalizations.. This allows farmers to take immediate action to prevent the spread of such behaviors.
Monitoring and Adjusting Conditions for Aquaculture and Sheds: Minor adjustments in factors such as humidity, temperature, space, and brightness can significantly influence crucial processes like breeding productivity. By monitoring these conditions, AI helps ensure optimal environments for animal welfare and regulatory adherence.
Optimizing Feeding Schedules: By analyzing data collected from monitoring, AI can help find the best feeding schedules to enhance productivity, product quality, and cost efficiency. Farmers can use advanced analytics to test various setups and identify the most effective feeding strategies, leading to overall improvements in farming productivity.
Enhancing Hatcheries :AI can improve hatcheries by ensuring optimal condition for embryo develpment, connected to incubators and sensors, AI systems analyze data to detect any changes that could affect embryo growth, allowing farmers to make adjustments and maintain ideal incubation conditions, enhancing overall hatchery efficiency.
Early Detection of Non-Hatchable and Infertile eggs: Combining near-infrared hyperspectral imaging with machine learning allows for early identification of non-hatchable and infertile egg, reducing unneccesary cost and optimizing hatchery space. When paired with sensors, these systems offer insights into how environmental conditions affect embryo development, helping to prevent waste and maximize productivity.
Determining Sex with AI: AI can potentially end the controversial practice of killing male chicks by enabling sex determination within the first few days of incubation. By using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) combined with AI models to analyze and categorize images, livestock producers can adopt a more ethical and efficient approach to sexing chicks.
Motion Sensor-Equipped Collars:They collect various data about cows, which is analyzed by AI in dairy automation systems. This data reveals information on heat stress, changes in feeding efficiency, and estrus cycles. During estrus, hormones affect the cow’s behavior and movement—such as standing heat, where the cow may stop moving to allow others to mount her. AI compares recent movement data with historical data to predict ovulation, which typically starts 24 to 32 hours after standing heat. This allows farmers to prepare for artificial insemination at the optimal time.
Robotic Injection Systems:Modern dairy farms use robotic injection systems to administer vaccines and reproductive drugs efficiently, avoiding the need for significant labor and training investments. Integrated with dairy automation systems, these robots read ear tags to access the cow’s health and vaccination history.
Facial recognition technology: It simplifies monitoring an entire herd by eliminating the need for device installation. It enables individualized monitoring of group behavior, early detection of lameness, and accurate recording of feeding habits, all with minimal human interaction.
Automatic milking machines: It bfeature sensor cups that attach individually to each teat. They can automatically clean and sanitize the teats and detect the milk’s color, impurities, and quality. If the milk is deemed unfit for human consumption, it is diverted to a separate container. Automatic Robot Feeder: This device provides farm animals with a concentrated mixture of roughage tailored to their nutritional needs. Additionally, a scraper robot cleans slatted floors by pushing and scraping away slurry, navigating narrow spaces effectively to maintain clear, clean surfaces.
AI in Genomics and Gene Editing: AI is revolutionizing genomics, the study of an organism’s complete set of genes. By enhancing DNA sequencing and analysis, AI systems make these processes faster, more affordable, and more accurate. This enables better decisions regarding care, disease susceptibility, and mutation-related risks. Successful applications include “editing out” disease-causing genes and “editing in” genes for high-yielding, disease-resistant animals.
AI for Predicting Breeding Values: Machine learning techniques like decision trees and artificial neutral networks (ANNs) are becoming increasingly popular in agriculture for their speed, power, and flexibility in handling classification and prediction tasks, particularly in nonlinear systems. These methods are used to detect mastitis, identify estrus, and understand selection criteria. They also analyze breast feeding curves, interpret somatic cell count data, and assess reproductive management efficiency
Futuristic Applications of AI : While the full impact of AI on traditional family farms remains uncertain, the emergence of adaptable technology from new agritech companies suggests that the “digital farm” may be closer than anticipated. As consumer pressure shifts focus from environmental impact to animal welfare. Utilizing AI and new technologies will be crucial for optimizing livestock farming and enhancing animal welfare, which is increasingly important to consumers and essential for the sustainability and profitability of agriculture.
Conclusion: AI can significantly enhance efficiency in livestock farming by identifying and tracking animals, and predicting optimal feeding and breeding strategies. A proposed AI model outlines steps for implementation, addressing various challenges. AI models analyze data from sensor, imaging, and digital systems to provide insights into animal health, predict disease outbreaks, and offer early warnings of potential threats. The model should be customized to the farm’s specific needs, encompassing data acquisition, model development, validation, deployment, and maintenance. Regular monitoring and updates are crucial to ensure continued accuracy and reliability