Role of Different Poultry Feed Additives and Supplements in Commercial Layer & Broiler Poultry Feed
The diet of animals and humans contain a wide variety of additives. However, in poultry diets, these additives are primarily included to improve the efficiency of the bird’s growth and/or laying capacity, prevent disease and improve feed utilisation. Any additives used in feed must be approved for use and then used as directed with respect to inclusion levels and duration of feeding. They are also specific for the type and age of birds being fed.
Common feed additives used in poultry diets include antimicrobials, antioxidants, emulsifiers, binders, pH control agents and enzymes. Sometimes diets will also contain other additives used in diets for humans and pets such as flavour enhancers, artificial and nutritive sweeteners, colours, lubricants, etc. Within each one of these classes of additives, there can be dozens of specific additives manufactured and distributed by a wide variety of companies. Again, all ingredients and additives must be noted on the label and their use and inclusion levels meet the standards as defined by law. In some instances, additives are added to the animal’s diet in order to enhance their value for human consumption, but mostly this is accomplished by use of natural ingredients containing significantly higher levels of these nutrients that can be deposited directly into meat and eggs. This fact sheet will highlight a few important feed additives and their use in the poultry industry.
Global poultry feed market is currently showing the increased demand for protein and nutrient rich food like poultry egg, meat and meat products. If farmers are to be able of feeding approximately 9 billion people in the world by 2050 then they must find some methods to produce relatively economical high-quality products. The cost of the feed accounts for approximately 70% of the cost in poultry production (Cooke, 1987). Soya bean and maize are widely utilized by poultry farmers in India as the main feed. These satisfy only minimum nutritional needs of birds. Major challenge in global poultry production is food safety, environmental issues, standardizing welfare standards, ban of nutritive antibiotics, gut health, feeding rich in fibre ingredients and maintaining high efficiency of production. There is also the problem of monitoring of the poultry feed mixtures. Preparing poultry rations is not just a case of milling and mixing cereals, inclusion of additives is as important (Kataria et al.,2005).
Efforts to produce human food from animal sources efficiently and economically open immense opportunities to the nutritionists for continuous research on poultry feed and feed additive supplements. Feed additives increase quality, digestibility, palatability, and nutrient availability of the feed. They also improve animal’s growth, performance, immunity, and gut health if chosen wisely (Koopman et al.,1984). Additives in feed improve feed conversion efficiency, reduce the stress, maximize the profit and lower the cost of poultry production. Thus, feed additives give significant rewards in intensive poultry production in today’s competitive environment. The use of feed enzymes, phytogenic, prebiotics and probiotics has acquired dynamic velocity in poultry feeding.
Poultry farmers spend a significant amount of time focused on finding chicken feed ingredients that provide high-quality nutrition to their flocks. Modern methods of farming have introduced the ability to enhance the nutritional properties of chicken feed ingredients with supplements and additives. This is good for both the farmer and the feed manufacturer or producer. High-quality feed additives enhance the overall economics of feed for manufacturers and producers.
Some of the most common additives include pellet binders, moisture optimizers, and grain and feed conditioners. For farmers, the benefits of chicken feed additives are two-fold: (1) longer shelf-life and preservation of feed, and (2) enhanced nutrition that improves the value of poultry.
Chicken Feed Ingredients
The seven basic chicken feed ingredients
- Cereal grains
- Cereal byproducts
- Fats and oils
- Protein meals
- Miscellaneous raw ingredients, such as tubers and roots
- Minerals and vitamins
- Feed additives
Cereal grains typically make up the greatest amount of chicken feed ingredients. It’s a cost-effective component that helps fulfill energy requirements for chickens. Unfortunately, cereal grains are highly susceptible to mold, bacteria, and rot. Grains that are improperly stored can harbor mycotoxins which can negatively affect the health and growth of the chickens. Thanks to the preservation properties of feed additives, cereal grains can be used as ingredients in chicken feed without going bad during extended periods of storage.
Key nutrients that need to be supplied to flocks through chicken feed ingredients include amino acids that are contained in proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Fats, oils, and protein meals comprise the remainder of a chicken’s dietary energy requirements.
How Supplements Improve Health and Performance
Supplements help increase the productivity and health of chicken by increasing the nutritional output provided by the feed itself. Supplements can save farmers and feed manufacturers substantial amounts of money by increasing yields and prolonging shelf-life. These features allow for an easier transportation process and result in less wear and tear on production machinery.
Common additives and supplements:
- Toxin binders
- Mold inhibitors
- Antioxidants
- Antimicrobials
- Direct fed microbials
- Flavors
- Organic minerals
- Feed conditioners
- Pellet binders
- Digestive enzymes
- Feeding effectors
- Anti-stress agents
- Acidifiers
Improving Chicken Feed Ingredient Value
Effective supplements will make feed processing more profitable for livestock feed manufacturers by boosting the overall value and nutritional qualities of the feed they produce and sell to farmers and bulk buyers. These nutrient-rich supplements can also help sick and stressed birds return to optimal health. An added benefit of supplements is that they are easy to apply and can limit metal pollution through chicken’s fecal waste.
Feed Additives-their Inclusion level in Poultry diet:
Feed additives are Non-nutritive substances, ingredients or combination of ingredients added to the basic mix in micro quantities to fulfill the specific need of animals (Hutjens,1991). Various Feed Additives and their inclusion levels in % of poultry diet are Trace Mineral Mixture 0.20%, Vit.A,B2,D3,K 0.05%, Vit.-B complex 0.05%, Choline chloride 0.10%, Probiotic 0.05%, Enzymes 0.05%, Toxin Binders 0.05%, Coccidiostats 0.05%, so total 0.60% feed additives can be added in poultry diet.
Broad Classification of Feed Additives:
- Growth Promoters– Antibiotics, Arsenicals; Natural Growth Promoters like Prebiotics, Probiotics, Symbiotic, Organic acids, Phyto biotics, Enzymes, Vitamins and Minerals.
- Disease preventing agents– Coccidiostats, Anthelmintic.
- Auxiliary substances- Antioxidants, Hormones, Pellet binders, Electrolytes, Flavoring agents, Pigments, Emulsifiers, Feed preservatives.
According to EFSA (European Feed Standard Agency) there are 5 categories of feed additives including Zoo technical (enzymes, probiotics, prebiotics, and Phyto biotics); Nutritional (Vitamins and Amino acids); Technological (Organic acids, Antioxidants, Pellet binders); Sensory additives (flavors) and Coccidiostats.
Market Share of Global Poultry Feed Additives :
The Broilers feed segment has the largest market share in poultry feed while Antibiotics segment has the largest share of poultry feed additives.
Various Feed Additives used in Poultry:
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are soluble organic substances produced by microbes, having bacteriostatic or bactericidal action (Frost et al.,1991). These are included in poultry diet at low concentration (1 to 50 mg/kg feed). Chicken fed with Vegetable protein gained more weight when antibiotics mix at 5-10 mg/kg of feed (Castanon et al.,2007). They have metabolic effect on various enzyme systems required for transport of nutrients across intestinal cell wall. Antibiotics have Nutrient sparing effect which decreases Vit. D and Mn requirement. They help in inhibition of toxin-producing bacteria by depressing bacterial urease production leading to avoid NH3 toxicity. ‘Disease level’ theory of antibiotics against sub-clinical infection (intestinal bacterial loads) leads to gut thinning resulted in healthier intestinal walls; suppressing the ‘Bad bugs’ (E. coli, Salmonella) and allow the ‘Good bugs’ for efficient digestion of feed in GIT (Parks et al.,2001; Vander et al.,2000). The well balanced avian intestinal microflora contains more than 90% gram+ve bacteria in which mainly are lactobacillus.
Non Ionophore antibiotics are Tetracycline, avoparcin, Zinc bacitracin, virginiamycin, flavomycin, tylosin etc. (Chowdhury et al.,2009) are mainly used in poultry diet. Due to some limitations like residues in chicken meat and eggs transferred to human, bacterial resistance to antibiotics, consumer awareness. Antibiotics Growth promoters are banned in some countries like European Union Legislation since 2006. So many alternatives are used in place of antibiotics like natural growth promoters, Phyto biotics etc. Arsenicals improve growth of broilers causing bright red combs and wattles due to dilator effect on capillaries and they also have the antimicrobial properties.
Exogenous Feed Enzymes
Enzymes act as catalysts which help in digestion and nutrient utilization that otherwise go unused from body. They reduce anti-nutritional effects of non-starch polysaccharides in plant cell wall components present in cereal grains and oil seeds (Ravindran & Son,2011; Bedford, 2000). They also reduce the gut content viscosity. A better protein and amino acid digestibility can be seen in very young birds when given protease with feed in which endogenous proteases function remain not so optimal (Walk et al., 2018). E.g. β-glucanases, β-Galactosidases, Cellulases and Phytases, Xylanases, Proteases, Lipase, Amylases. A multi-enzyme preparation with cellulolytic and proteolytic properties is used in advanced nutrition. E.g. Avizyme series 1500. Feed enzymes like β-glucanases and xylanases have enabled Barley or Wheat up to 50-60% in poultry diets.
Hormones
In some countries use of hormones is banned due to much public concern because of residues in poultry products. Hormones have high potential for increased protein and reduced fat deposition (Buttary and Dawson,1987). Thyroxin is given in form of Iodinated casein at 100-200mg/kg feed in layers for improved egg production. Thiouracil (anti-thyroid drug) in combination with DES (diethyl stilbesterol) improves finish and market quality without depressing growth rate. Dienestrol diacetate is only hormonal Feed Additive that is currently approved at 0.0023-0.0035% in feed of broilers only. ‘Panchgavya’ are rich source of minerals as well as hormones.
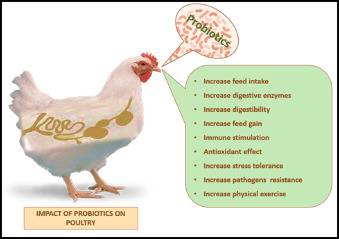
Probiotics/ Direct Fed Microbial (DFM)
Probiotics are live culture of nonpathogenic microbes promoting the gut health (Fuller, 1989). These beneficial bacteria compete and secure the attachment sites in gut wall by competitive exclusion of pathogenic harmful bacteria and improve the intestinal microbial balance. E.g. Lactobacillus acidophilus, Streptococcus faecium, Bacillus. Live yeast culture with Lactobacillus ‘Lactosacc’ was given in broilers (1kg/ton feed) which showed improved weight gain and FCR, reduced mortality and morbidity. Probiotics having Pediococcus acidilactici and Saccharomyces boulardii acts as prophylactic against coccidiosis in birds. Probiotics neutralize the microbial toxins by producing substances like lactoferrin, fumonicins (Patterson & Burkholder, 2003). They have bactericidal activity like Lactobacillus produces lactic acid reducing the PH to a level that is unfavorable for E. coli. In addition, H2O2 and inhibitory substance ‘Acidolin’ are produced that are harmful to coliform bacteria.
Prebiotics/ Oligosaccharides
Prebiotics are non-digestive feed ingredients which selectively enhance growth and activity of bacteria already present in the GIT, thus improve the host health and assist in immune modulation (Gibson and Roberfroid,1995). E.g. Fructo oligosaccharide (FOS) in, Mannan oligosaccharide (MOS), α Galacto oligosaccharide (GOS), Trans Galacto oligosaccharide (TOS). Prebiotics and Probiotics together called as ‘Synbiotics’. Mookiah et al.(2014) found more beneficial growth rate of birds with supplementation of synbiotics in the diet compared to either probiotic or prebiotic alone. Pathogenic bacteria in gut which have surface compounds called as Lectin. This lectin bounds with the free carbohydrate oligosaccharides and prevent the pathogenic microbes to attach to gut wall and flow out these from gut along with the digesta.
Phyto biotics
Phyto biotics are natural growth promoters derived from herbs, spices or other plants which are incorporated into feed. They have preservative and medicinal properties (Windisch et al., 2008; Bravo et al., 2014; Pirgozliev et al., 2015). The inclusion of Phyto biotics in feed reduce palatability of diet due to pungent odour which decrease the feed intake without changes in body weight gain, leading to an improved FCR. These stimulate the secretion of digestive enzymes and increase the apparent ileal digestibility (AID) of nutrients in broilers. They have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, coccidiostat, anthelmintic, antibacterial, antiviral activity and immunity boosting properties. They help in reduction of NH3 emission in poultry sheds by decreasing wet litter problems. Phyto biotics have wider spectrum of action, no bacterial resistance, no side effects, safe and environment friendly against the use of antibiotic growth promotors (Dibner & Richards, 2005). Supplementation level of essential oil and single plant ingredients is (0.02-1.0 gm./Kg feed) and of dried products and plant extracts is (0.1 and 40 gm./kg feed). Herbs like Mint, Saffron, Oregano, Fennel, Coriander, Turmeric, Thyme, Aloe vera, Celery seed, parsley, Chervil, Basil ; Essential Oils from Eucalyptus leaf, Cinnamon bark, Oregano flower, Pepper seeds, Garlic bulb, ginger roots, lemon and orange fruit peels; Oleoresin (Oil+ Resin) can be used in poultry feed.
Acidifiers/ Organic Acids
Organic acids are usually added as feed preservatives for preventing food deterioration and extending the shelf life of perishable food ingredients (Parks et al.,2001; Abdel-Fattah et al.,2008). Ca-formate (1.3%) is added which is converted to formic acid in their crop. Mixture of fumaric acid and salt of Butyric acid, propionic and lactic acids supplementation at 520 PPM improve egg production, egg size, shell thickness in layers. Benzoic acid at 0.2% may have positive influence on growth in broilers. They have antimicrobial effect on harmful gut microbes by reducing gut PH; improve consistency of layer droppings resulting in fewer dirty eggs; better Ca absorption and eggshell quality; reduce the effects of Ascites in poultry.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants prevent the fat oxidation and help to avoid rancidity of fat in poultry products. They also mop up the free radicals in the body and usually added at 0.01%/kg feed (Surai et al.,2019). E.g. Natural antioxidants are Vit. E (most active), Vit. C, Selenium, Rosemary extract, carotenoids and flavonoids. Synthetic antioxidants are Butylated hydroxy anisole (BHA), Butylated hydroxy toluene (BHT) and Ethoxyquin. Vit. E and Rosemary extract are of good consumer appeal. Certain metals like Cu and Fe are active catalysts of oxidation, so they need to be removed by some compounds called as Sequestrants or metal scavengers like Ca salt of EDTA.
Flavouring Agents and Pigments
Flavors are used to improve palatability and food appeal. E.g. Sugars (Jaggery), Skim milk powder, MSG (Mono Sodium Glutamate), Fennel, Vanilla etc. Chickens have a sense of taste but a very limited ability to smell (Landenmaier and Kare,1959). Pigments are used in preparation of designer poultry products to satisfy consumer preference. Xanthophyll present in yellow maize and Lucerne meal at 2-3% level produce deep yellow pigmentation in body and egg yolk. Bixin produces red yolk and Canthaxanthin produces orange colored yolk and carcass skin (A.R. Sams and Hirschler,2005). Carotenoids and Xanthophyll’s also have antioxidant and immunomodulatory functions. Okra meal can be used to provide pigment in broiler diets.
Nanoparticles as Feed additive
Nanotechnology helps in development of novel ‘Silver-Silica’ based composite material having good antimicrobial properties. It also helps to reduce size and increase surface area of Cu-Nanoparticles compared to the bulk material leading to a variety of applications like chemo sensors, surfactants. Nanotechnology is used in the application of Nano sized minerals as a tool in the field of Mineral Nutrition.
Anticaking/Free Flowing Agents and Deodorizing Agents
Anticaking agents are anhydrous substances used in preparation of mash type feed. They avoid the problem of cake or lump formation by picking up moisture without themselves becoming wet. E.g. Salts of short chain Fatty acids (Ca stearate), Ca phosphate, MgO, Kaolin. Odor of litter in poultry is a problem to farmers due to urea or uric acid present in urine and faces of Poultry. Urea is hydrolyzed by urease into NH3. ‘Yucca shidigera’ extract in diet as deodorizing agents blocks the action of urease and avoid NH3 toxicity.
Pellet Binders
Pellet binders enhance the firmness of pellets usually added at 2.5% of the diet. E.g. Sodium Bentonite (Clay), Lignin, Molasses, Guar meal. Lignin is mostly used. They reduce feed dust in feed mill, help pellets better to adhere, improve press capacity and die life of pellets, helps in more control over additions of fat and moisture (Anonymous,1983; MacMohan,1984). Incorporation of food-grade surfactants into mash feed can enhance the overall conditioning of the feed during pelleting by reducing the surface tension of water. They also have antimicrobial properties. E.g. Alkyl benzene sulfonates, lauryl ethylene oxide, ethmoid C-15.
Sodium Bicarbonate for Poultry
NaHCO3 is used to potentiate coccidiostats and to improve weight gain, livability and processing yield under stress condition. It is mixed in broilers feed at 1.8-2.7kg/ ton, in layers feed at 1-1.8kg/ton, during heat stress at 3.6-4.5kg/ton. It is usually given via water rather than the feed.
Emulsifiers
They help in fat digestibility in young chicks because of limited fat digestion in them due to low lipase and low bile production. E.g. Bile salts (natural emulsifier), Soy-lecithin, Lysolecithin, Milk derived casein.
Chelates
Chelate is cyclic compound which is formed between an organic molecule like amino acid and a metallic ion or inorganic molecule (Hudson et al.,2004). Chelating agents like EDTA are used to increase the bioavailability and absorption of certain minerals like Zn. Various Types of chelates are Metal specific amino acid complex, Metal Amino acid chelate, Mineral proteinates, Mineral polysaccharide. Limited work has been done in India on use of chelated minerals. Majority of animals do not receive even low cost ‘Common salt’ in India.
Methyl Donors
They spare or alternate the EAAs, vitamins like Vit.B12, folic acid. E.g. Methionine (costly), Betaine (cheaper), Choline (cheapest). Betaine or DMG (dimethyl glycine) at 1gm/kg diet enhance digestibility of dietary fat and thus improve meat yield in broilers and avoid Broiler Ascites syndrome (Zulkifli et al.,2004; Ratriyanto et al.,2009). It is also used during heat stress in poultry birds. L-carnitine and Ractopamine are also used because of their lipolytic activity and beneficial effect on growth and performance of birds.
Chito-Oligosaccharide (Chitosan) and Sodium Metabisulphite
Chitosan contains reactive functional groups like amino acids and –OH groups. They have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antitumor, immunostimulatory and hypercholesteremic properties. They are alternate of antibiotics. Sodium metabisulphite causes oxidative-reductive depolymerization of starch polysaccharides in Sorghum diet which enhance the apparent ME, N2 corrected AME, feed conversion efficiency in broilers.
Coccidiostats
These are used to control coccidian infection in poultry intestine. E.g. Bifuran, Amprolium 25% (Aprol), Nitrofurazone, Furazolidone, Maduramycin, Salinomycin, Diclazuril (Clinacox), Monensin and Lasalocid.
Anthelmintic
Intestinal worms like (Ascaris, Heterakis, Capillaria, and Taenia) are killed by use of vermifuges. Piperazine marketed under the name ‘Wazine’ and Fenbendazole under the name ‘Aquasol’ for poultry. Feed thru larvicides contain insect development inhibitors are used in feed. Anthelmintic require more than 1 administration (1st kills those worms which are present in the body and 2nd kills those which hatched from eggs after initial dose).
Antifungal Additives and Mycotoxin Binders
Best method of controlling fungal infestation is to dry all feeds below 12% moisture. Mold inhibitors like Formaldehyde should be sprayed in the form of fine mist over finished feeds before packing of feed during storage. 3 main toxin producing fungi are Aspergillus, Fusarium, Penicillium. These fungi produce many Fungal toxins like Aflatoxin, Ochratoxin, Zearalenone, Trichothecens (Saleemi et al.,2017). Toxin binders are used for the removal of mycotoxins through feces. E.g. Activated Charcoal, Synthetic Zeolite, Mineral clay, Sodium bentonite (Bhatti et al.,2016). Common commercially available mycotoxin binders are Mycosorb, Mycofix, ProSid and Mycoad. Toxicity of Aflatoxin in feed can be reduced by using UV light, by mycotoxin binders or by exposing feed to anhydrous NH3 under pressure (Sana et al.,2019).
Feed additives: Additives are never nutrients. They either singly or in combinations are added to a basic feed, usually in small qualities for the purpose of fortifying these with certain nutrients or stimulants or medicines. Often they are called “non-nutrient” feed additives.
Following are some modern feed additives used for poultry –
Additives that promote feed intake or selection
Additives that Enhance the colour or quality of the marketed product
Additives that facilitate digestion and absorption
Additives that alter metabolism
Additives that affects health status
|
Recommended range of proportion of poultry feeds
| Ingredients | Proportion (% by wt of materials) |
| Grain and Seeds | |
| Bajra, bajra (Pennisetum typhoides) | 10-15 |
| Barley(Hordeum vulgare) | 5-10 |
| Black-gram (Phaseolus mango) | 10-15 |
| Chinna, cheena (Panicum miliaceum) | 10-15 |
| Kulthior horse-gram (Dolichos biflorus) | 10-20 |
| Jowar,Cholam (Sorghum vulgare) | 10-15 |
| Oat (Avena sativa) | 5-20 |
| Arhar (Cassia tora) | 5-10 |
| Ragi (Eleusine coracana) | 10-20 |
| Yellow maize | 15-50 |
| Grain by-products | |
| Arhar chuni | 10-15 |
| Gram chuni | 10-15 |
| Black-gram chuni | 10-15 |
| Maize grit | 10-15 |
| Maize-gluten meal | 10-20 |
| Rice bran and polishings | 10-30 |
| Wheat bran | 10-15 |
| Minerals, Vitamins and antibiotics | |
| Common salt | 0.3-0.5 |
| Dicalcium phosphate (fluorine content not exceeding 0.5%) | 1-2 |
| Limestone | 1-3 |
| Oyster shells | 1-3 |
| Vitamins (mineral stabilised) | As recommended by the manufacturer |
| Manganese sulphate | 0.02-0.3 |
| Antibiotic feed supplement | 0.1-0.5 |
| Oil-cakes and meals | |
| Copra cake, coconut cake | 5-10 |
| Cottonseed oil cake (decorticated) | Up to 5% by weight |
| Groundnut oil cake (decorticated) | 15-3 |
| Guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba)meal | Up to 5% by weight |
| Safflower (Carthamus tinctorious)cake | 10-15 |
| Mustard cake: Expeller | 10-20 |
| Deoiled | 25-50 |
| Salseed cake (Shorea robusta) | 0-5 |
| Sesamum (Sesamum indicum orientale)cake | 10-20 |
| Soyabean meal | 10-20 |
| Karanja deoiled cake (Pongamia glabra) | 7-8 |
| Tubers and roots | |
| Tapioca flour | 10-25 |
| Greens | |
| Berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum) leaf-meal | 3-5 |
| Lucerne (Medicago sativa) leaf-meal | 3-5 |
| Waste materials and industrial by-products | |
| Brewers’grains | 2-5 |
| Dried yeast and yeast sludge | 2-5 |
| Mango-seed kernel | 5-10 |
| Molasses | 5-10 |
| Penicillin mycelium residue | 5-15 |
| Silkworm pupae (freed from membranous covering) | 5-10 |
| Bloodmeal | 3-5 |
| Animal products | |
| Fish-meal | 5-10 |
| Liver residue | 5-10 |
| Meat-milk and meat-scarp | 5-10 |
| Skim milk (dried) | 5-10 |
| Blood meal | 3-5 |
Antinutritional Factors and Digestibility
Many feedstuffs contain antinutritional factors that interfere with the utilization of dietary nutrients. Some reduce protein digestibility, bind to dietary nutrients, or damage the gut wall. Soybeans, for example, contain protease inhibitors that inhibit the activity of the enzymes needed to digest protein. Raw soybeans contain trypsin inhibitors, but these antinutritional factors are inactivated by the heat generated in the production of soybean meal or when whole soybeans are roasted.
Corn and soybean meal are commonly used in commercial poultry diets in the United States. With the ever higher prices for corn and soybeans, many producers and companies are looking at alternative feed sources. Although several alternatives exist, most of them contain one or more antinutritional factors.
-
- Wheat containsxylans (a type of pentosan), substances that can increase the viscosity of the gut material (digesta), thus reducing the level of nutrients that can be absorbed. Although the increased viscosity shows nutrient flow through the intestines, it also insulates the nutrients from exposure to intestinal microvilli, reducing the absorption of the nutrients. Signs of high viscosity digesta typically manifest as pasting of material around the event, especially in chicks. The effects of pentosans can be corrected by supplementing the diet with enzymes, xylanases, that are able to digest xylan.
- Sorghum (milo) contains tanninsthat bind with various proteins, reducing their digestibility. Different sorghum varieties have different tannin levels, so the type of sorghum used in feed is important. Generally the darker the outer seed coat of the sorghum variety, the higher the tannin content. Birds will refuse to eat grain with high levels of tannins.
- Barley contains moderate levels of trypsin inhibitors, but the major problem with barley is the level of beta-glucans. Similar to xylans, beta-glucans increase the viscosity of the digesta, thus reducing the digestibility of nutrients. Again, the adverse effects of the beta-glucans can be reduced with the use of feed enzymes.
- Canola meal contains sinapine, which causes a problem only for brown-egg layers. When canola meal is used in the feed for these layers, the eggs have a fishy and offensive odor.
Mold Contamination and Mycotoxin Reduction
The cereals frequently used in poultry diets are subject to mold growth. Mold contamination can occur in the field or during post-harvest handling, storage, and processing. Mold inhibitors such as organic acids are used to prevent mold growth, but they are not effective against the mycotoxins that molds produce. Mycotoxins are poisonous chemical compounds as secondary metabolites by actively growing molds. There are more than 3009 types of mycotoxins that affect animals, but aflatoxin, vomitoxin, zearalenone, ochratoxin, and trichothecenes are the most common. Even if the mold is no longer visible, the mycotoxins remain. For this reason, many poultry feeds contain a mycotoxin binder that binds to the mycotoxins and prevents them from being absorbed through the gut and into the bloodstream. Common mycotoxin binders are Mycosorb, Mycofix, ProSid, Mycoad (which appear on the Organic Materials Review Institute (OMRI) list of approved substances for organic poultry production) and Toxisorb.
Maize/Corn–
- Maize is the major energy source used in Poultry Feed diets in most of the countries because of its easy availability, easy storage & high-energy value and high digestibility.
- Dry maize contains the highest amount of energy ME 3350 kcal/kg & 8-13% of Crude Protein. In very dry state its values can be increased.
- Maize can be included up to 70% in poultry Ration.
- While Purchase of Maize remember maize, Maize must be dry, fungus free and moisture content should be then 13.5 %.
- Less moisture content of Maize in Poultry Feed will accelerate good growth rate in Broiler Birds.
How to check Maize Moisture at home –
To Test Moisture content, you can use a moisture meter which is highly recommended.
You can use a traditional method. Poultry Farmers can use a simple method to check if their maize is dry enough for storage by the use of an empty transparent bottle and some normal salt. Before Purchase maize, put a handful of Maize and ½ handful of common dry table salt in a dry bottle. Shake the bottle for 2 -3 minutes. Allow the grains to settle at the bottom of the bottle. If the salt sticks onto the walls of the transparent bottle, this is a sign that the maize is not dried well enough for storage. Otherwise Dry the maize and repeat the test until no salt sticks to the sides of the bottle. The maize can then be stored and there is no danger of it developing mould or aflatoxins during storage.
Soya bean meal for Poultry Feed –
- Soya bean meal contains 45-49% protein and is an excellent source of lysine, tryptophan and threonine but it is deficient in methionine.
- Raw soybeans may contain a number of toxic and inhibitory substances. These toxic, inhibitory substances and other factors in soya bean like saponins can be inactivated by proper heat treatment during processing. So it’s better to purchase from a reliable source. It can be included up to 35% in chick’s poultry Feed.
Use of oil in poultry Feed- Oil Are Rich in energy. Oils are also an important carrier for fat soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. A variety of fats and oils are used in Poultry Feed Formulation Like Palm oil, Sunflower oil, Rice Bran Oil, Soya Oil,canola,rapeseed oil, sunflower oil, linseed oil, palm oil, cottonseed oil etc. & Tallow or Animal Fat also used In Poultry feed formulation.
In practical Poultry Feed formulation, the level of oils rarely exceeds 4% in Poultry Feed Formulations.
Lime Stone Powder for poultry Feed-Lime Stone Powder is a major source of calcium or an important part in the Poultry Feed to maintain bone strength.
Dicalcium Phosphate poultry Feed- Dicalcium Phosphate is also an important source of calcium or an important part in the Poultry Feed especially for Vegetarian Poultry feed Formulation.
Before Understanding below Poultry Feed additive, please don’t get confused about large range of Feed Additive. All below Feed additives can be very easily purchased From a Single Poultry Supplement shop.
Sodium Chloride ( NaCl) poultry Feed– chickens need between 0.12% to 0.2% sodium in the Poultry Feed Formulation . If measured as NaCl or “salt,” it should be 0.4-0.6%.
Sodium is also available in Soybean meal & Maize but additionally Sodium Chloride is also added in poultry feed in different quantities depending upon Poultry Feed Formulation. Without salt, growth is slowed, and chicks are dull .Sodium deficiency can may cause birds to collapse and die suddenly; opening up the body cavity will reveal fluid accumulations around the lungs and heart. (Known as broiler ascites syndrome) .Appetite of Poultry birds may decrease & pecking behaviour (Birds biting each Other) may increase. So maintaining the Sodium Level is also Very Important.
Sodium Bicarbonate for poultry Feed-Broiler Poultry Feed Intake and growth rate can be improved by supplementing the diet with sodium bicarbonate. Bicarbonate ion and is associated with an increase in water consumption.
Some studies show that Sodium bicarbonate increases digestibility.
DL-Methionine for poultry Feed- It is actively involved in the synthesis of tissue proteins, a number of vitamins, hormones, and enzymes .Lack of methionine deficiency can cause leg dermatitis in chickens. It also improves Growth and Stress.
Lysine for poultry Feed- Sufficient amount of Lysine in Poultry feed Improves calcium Absorption, Growth and Reduce Stress-Lysine concentration significantly influences on the growth performance and feed efficiency. Inclusion of lysine in the diets and poultry It helps to justify the basis of low cost Poultry Feed formulation and also enables to balance the diet to meet the birds requirements more closely.
Threonine for poultry Feed- Improves Growth and Reduce Stress & also improves Breast meat.
Choline Chloride for poultry Feed– Choline Chloride helps in fat metabolism in the liver, i.e. utilization and outward transport of fat, so preventing abnormal accumulation of fat within hepatocytes – so-called “fatty liver.
Many studies shows that, after adding choline chloride, very good weight gain results in less feed consumption.
Trace Minerals Combination for poultry Feed-Many Companies Provide trace minerals for broiler feed formulation. But because of cost competition many companies don’t add Selenium and Chromium in sufficient quantities in trace minerals. So please cross check whether Selenium and Chromium is available in trace minerals in sufficient quantity or not.
In most cases you have to add additionally Selenium and Chromium of a reputed company as per recommended dose.
You can increase the dose of Trace Minerals 10 %. I personally found it helps to decrease mortality & improve performance.
Broiler Premix Vitamins for poultry Feed– I noticed many companies provides balance combination of all vitamins ,but because of cost competition ,many
Supplements for Poultry Feed
companies miss Vitamin E ,C and Biotin in the Broiler Premix, So never forget to add additional Vitamin Vitamin C and Biotin if not available in Sufficient quantity.
You can increase the dose of Broiler premix 10 %. I personally found it helps to decrease mortality & improve performance.
Mycotoxin Binder for poultry Feed– Traditionally many poultry Farmers use Toxin binder, it’s a good idea, but I personally recommend Mycotoxin Binder rather than Simple Toxin Binder. .
Mycotoxin binder is a substance that is added to Broiler Feed Formulation in order to trap Mycotoxins, preventing them from entering the bloodstream where they can cause serious harm to your Poultry’s Birds.
If you have any doubt about little down of Ingredients. While making poultry feed Using a Toxin binder along With Mycotoxin Binder is also a good idea to improve performance of Broiler Poultry Feed Formulation.
Many companies provide Mycotoxin Binder, easily available in the market.
Acidifiers for poultry Feed- The major purpose of using this acidifier in Poultry feed Formulation is to improve growth performance and better the profitability in poultry production. Acidifiers have multi usages in poultry feeds as they help in preservation to control microbial growth, reduction of the feed buffer capacity, inhibition of pathogenic bacteria and betterment of nutrient digestibility.
It is important that poultry birds keep a low gastric pH, so they can activate enzymes which are critical for protein digestion. This low pH also curbs pathogens. Pathogenic microbes compete with the birds for vital nutrients in feed and grow quickly which higher pH leading to harm in health and productivity of the birds. Acidifiers are very effective in decreasing bacterial load resulting less mortality at Poultry farm
Liver Tonic Powder for poultry Feed– Herbal/Synthetic -Liver Tonic Helps To Improve Liver Performance or Flush out toxins from the Body. It is highly recommended to add Tricholine based Liver tonic or Herbal Liver Tonic In poultry feed Formulation. It has been noticed broiler birds gain better weight gain.
Anticoccidials uses and precaution in poultry-
Anticoccidial defined as an antiprotozoal agents used for the prevention & control of coccidiosis are called Anticoccidial & Must be used with proper method of rotation & Shuttle every important things will be covered in this part. First understand the types of anticoccidials. There are many types of
1- Chemical /Synthetics Anticoccidial
Compound produced in the laboratory rather than natural ingredients or product synthesis from chemicals. So it’s often referred as chemicals
Robenidine
Ethopabate
Aprinocid
Clopidol
Decoquinate
Diclazuril
Dinitolmide ( zoaline)
Halofuginone
Nicarbazin
& More
2-Ionophore
a)-Monovalent Ionophores , b) Monovalent Glycoside C)Diavelent D) Combination of two Anticoccidials
a)-Monovalent Ionophores.
Monensin, Narasin and Salinomycin
Are highly reaction with Tiamulin Hydrogen Sulphate
Be careful while making poultry feed.
- b) Monovalent Glycoside.
Maduramicin and Semduramicin
3- Divalent Ionophores.
Lasalocid Sodium.
4-Mixed Anticoccidials.
It is defined as a mixer of two or more anticoccidials of either synthetic & chemical origin. Eg Narasin+Nicarbazine
Or Maduramicin with Nicarbazin.
Now a question arises here how and which to use. It Depends on the Climate of your Region. Sometimes it also depends on the severity of Cocci in a particular area.
Withdrawal period means, before selling birds all antibiotics & Anticoccidials will be withdrawn from poultry feed , so that no side effect on the people who consume the same chickens.
There are many way to use Anticoccidials.
Straight Method for anticoccidials in poultry feed –
Some Feed miller or Poultry farmers Follow the single Product use in Poultry feed from pre starter to Finisher Poultry feed. With a withdrawal period of 3–7 days. Most products are approved for use until slaughter.
As per my experience in dealing with Poultry Feed Mills , I personally don’t recommend this method.
- B) Shuttle Method for anticoccidials in poultry feed.
The use of one product in the, Prestarter,Starter feed and another in the grower Poultry Feed or Same anti coccidiosis in PrestarterStarter and another in the grower Poultry Feed for the purpose of prevention & control of coccidiosis is called a shuttle program .This programs mostly used for commercial broiler poultry Farming.
I highly recommend this & it is very effective in Poultry to control coccidiosis
- Rotation of anticoccidials .
Rotation of drugs may improve productivity. When a product is used continuously for a long time less efficacy of product has been noticed
Producers often notice a boost in productivity for a few months after a change of anticoccidial drugs at time of rotation period in the field.
In the rainy season and winter there is a wet litter issue in Poultry farm & Broiler Birds face maximum coccidiosis challenge Nicarbazin or Combination with Maduramicin & Nicarbazin & Combination of 2 Anticoccidial has been found more effective
In the summer months, coccidiosis challenge tends to be milder, so weaker Ionophores (mentioned above ) are used in this rotation program found successful.
In short use Different Anticoccidial in Starter/Prestarter and Different in Finisher Poultry Feed Formulation.
In Summer Ionophores Ionophores (Monovalent Ionophores , b) Monovalent Glycoside C)Diavelent ) should be used in Finisher & Chemical Anticoccidials should be used in starter
In the Winter or rainy season when there is a high chance of cocci at your poultry farm,then you can use Ionophore in Starter & You can use Combination with Maduramicin & Nicarbazin or Combination of 2 Anticoccidial has been found more effective.
And always Keep Changing the Anticoccidials maintaining withdrawal period as per norms of your country or manufacturer Guidance.
Gut Acting Antibiotics use in poultry feed – Healthy gut healthy business. A healthy gut is key to a healthy bird.A healthy gut is not only a gut without disease; a healthy gut is an effective digestive organ that can mount an effective defense against disease and cope with change.
The gut is the bird’s largest organ where digested feed and water are absorbed so disease-causing agents must be kept under control. The gut is also the organ that generates the most immunity.So keep it healthy and away from any disease is very important.
Zinc Bacitracin(ZB) ,Bacitracin Methylene Disalicylate (BMD) & Many many Gut antibiotics are available and should be used as per your country norms and Regulation to increase performance as per manufacturer guidance.
Broad-spectrum antibiotic Growth promoters – Antibiotics help make food safe by keeping chickens healthy and reducing bacteria entering the food supply.Responsible use of antibiotics helps keep chickens healthy and minimizes the impact on the environment. Antibiotics are used to fight bacterial infections
Chlortetracycline is commonly used in Poultry. It also works on gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
There are many alternatives available and antibiotics should be rotated after a couple of batches for more effectiveness & withdrawal period must be followed as per manufacturer’s guidance and rules and regulation of your country.
Anti-Mycoplasma Antibiotics in poultry feed-
Remember, healthy looking birds may already have Mycoplasma, it may take up to 3 weeks before birds start to look and act sick or they may never act sick but still carry the disease and infect other birds. Bird’s sick with MG may have similar signs to what people get with a cold: runny nose, cough or unusual breathing sounds, and swollen or puffy eyelids and face. Bird’s sick with MS may have problems standing or walking, a pale or discolored comb, blotchy skin, ruffled feathers and swollen joints and blisters. Also, birds may be quieter, eat less and lose weight.
So to maintain bird health Anti Mycoplasma Antibiotics are used in poultry.
In Poultry Feed Tylosin,Erythromycin,Tiamulin,Lincomycin are many more are used as per guidance of manufacturer and rules and regulation of your country followed by withdrawal period.
Xylanase use in poultry feed- Xylanases can can improve overall feed efficiency
, thereby lowering production costs by reducing gut viscosity and increasing the access of digestive enzymes to the contents of plant cell walls in the diet.
Further benefits include increased boiler uniformity and a reduction in litter moisture content resulting in Less Formation of Ammonia Gases at Your Poultry farm.
Phytase uses in poultry feed-There is Huge amount of Phosphorus is available in poultry feed but not utilized by the broiler birds. After adding phytase to the Poultry Feed formulation, Extra phosphorus is easily available to poultry birds and less quantity of phosphorus is required to be added. It Lowers the feed cost and also helps to unlock many other nutrients for the poultry birds.
If more phosphorus is available naturally, then less of this substance has to be added to the diet. This greatly reduces feed costs.
It is available in the market in 2500 I.U, 5000 I.U., and 10,000 I.U.
You can increase the dose of Phytase. Upto 1.5 to 2 times.
The recommendation is around 100 gram / Ton of poultry feed of 5000 I.U
But you can increase the dose 150 gram to 200 gram /ton of poultry feed.
Copper Sulphate uses in poultry feed– Copper Sulfate for chickens has always been working as an anti-fungal and mould inhibitor in Poultry Feed Formulation. FCR is very much improved in Broilers
Probiotics uses in poultry feed- Poultry probiotics are defined as live microorganisms promoting enteric microbiota balance. Probiotics help to maintain a healthy gut & better immunity. It’s Just like giving Curd to your birds to improve productivity.
So you should choose a combination of many probiotics, easily available in the market.
Emulsifiers uses in poultry feed-Emulsifiers are used in poultry nutrition for improving poultry performance, digestibility of the nutrients, especially fats.
Emulsifiers are the best way to improve oil digestion resulting in better performance of Poultry Birds.
Antioxidants uses in poultry feed- Using Good Antioxidant is very much important otherwise oxidation can
Destroy fat soluble vitamins,
Reduce the digestibility of fat,
- Reduce the energy content of the feed
- Antioxidants slow down the oxidative process by sacrificing themselves for consumption by free radicals before the fat or vitamin molecules can be attacked.
In Short Antioxidant Maintain Feed Quality for a long Time by saving Feed from Oxidation.
MOS( Mannan-oligosaccharides) uses in poultry feed- MOS acts as prebiotics, Food of Probiotic. It also acts as an Immunomodulator and also helps Combat Many Toxins present in Poultry feed.
Turmeric Powder uses in poultry feed– It has been found that the feeding of turmeric powder in the poultry diet helped to improve the morbidity and mortality of broiler Poultry Feed. It is also proven that the use of turmeric in poultry feed is helpful for the public health with no side effects. It is also helpful for the poultry farmers, who are not able to use antibiotics.
Betaine uses in poultry feed –In Summer Can be added to reduce stress.
Many Poultry Farmers Don’t Get Best Results, when they make feed on their own Poultry Feed Formulation.
So below Precautions & Tips Should be taken care While Making Own Poultry Mash/Crumbs Feed.
Tip1- Every Manufacturer has different Dose of below Products. So Dose of below Products are As per Manufacturer Recommendation. Companies usually mention dose and sometimes also mention maximum and minimum dose.
2-If Your vitamin Premix Does Not contain Chromium ,Selenium,Biotin,Vitamin C or Vitamin E then you must add additionally as per manufacturers recommended dose.
In Hot Climate or at time peak summer in Hot Areas Betaine also should be added in poultry feed as per manufacturer recommendation. Betaine can be added in winter also it increases carcass yield & breast percentage.
3– Pre Starter Poultry Feed Formulation is recommended till the Birds reaches around 400 Gram. Starter Poultry Feed Formulation is recommended up to 1200 Gram and Finisher Poultry Feed Formulation is recommended up to selling of Birds.
4– Always Have Sufficient Advance Stock of each and every Ingredients.
5– Some Anticoccidials React with Antibiotics. Example- ( Salinomycin reacts with Tiamulin Hydrogen Fumarate. So when Changing Different Anticoccidials , discuss with some consultant.
6-For Poultry Feed mixing, farmers are advised to use a Good Quality mixer .Never use a shovel to mix feed because the ingredients will be unevenly distributed.
7-Phytase enzyme dose is recommended 1.5 times extra of Company recommendation in Poultry Feed. (Example if any company recommends 100 gram dose, you can increase the dose 150 gram.
8-Poultry Feed must be grind well, Large Poultry Feed particles don’t have better digestibility.
9-Poultry Feed must be mixed properly & oil mixing also should be well. First mix oil and all Medicine/supplements in a few feeds then mix with complete feed.
10-While making Poultry Feed, not a single product must be missed & to be mixed in Recommended dose.
11- Every Antibiotics & Anticoccodials have its Withdraw Period. So before selling birds withdraw Antibiotics or Anticoccidials before selling birds. As per recommendation of manufacturer or as per your country/Region Norms.
12- Every Product to be used in Poultry feed must be purchased before checking of Expiry date.
13-Always use the products of a well reputed company.
14- It is always recommended to use crumbs feed, sourced from a good company than shift to your Own mash feed.
15- Never shift from one type of Poultry Feed to another type of feed immediately. Example- If Shifting from crumbs to other feed. First mix the crumbs and mash feed by Ratio of 50%-50% and feed this feed for minimum 1 day.Then shit to mash Poultry Feed. Do the same while shifting to Pre starter to Starter & Starter to finisher Poultry Feed. Motive is not to provide immediate change in energy and protein.
16- While purchasing all the ingredients for Poultry Feed like Maize, Soyabean DOC and oil must be properly checked. Soybean DOC & Maize must be free from Fungus & Dry, to be purchased very carefully with strict precautions. Moisture in Maize is less than 14 % is recommended & moisture in Soybean DOC around 11% is recommended.
17-Never Purchase used bags for storage of Feed Bags to Store Poultry Feed. Bags must be purchased to avoid Contamination.
18-Poultry Feed & all Supplements must be stored in a well dry place and avoid direct Sunlight.
19-Antibiotics must be used as per your country/Region norms. If you’re Country’s Government doesn’t allow any antibiotics, never violate Rules.
20-Antibiotics must be used after Consultant Approval.
21- Antibiotics also should be changed after Couple of Batches.
22- Anticoccidials should be changed after Couple of Batches.
| Nutritional Standards For Broilers | |||
| Parameters | Prestarter | Starter | Finisher |
| Crude Protein %
ME (Kcal/kg) % Dig Lysine % Dig Methonine % Dig M+C % Dig Arginine % Dig Threonine % Dig Tryptophon % Calcium % Available Phosphorus % Sodium (Min.) % Potassium (min) % Chloride (max.) % Na++K-Cl mEq |
23.00
3000.00 1.21 0.54 0.88 1.25 0.80 0.19 0.90 0.50 0.16 0.55 0.30 250.00 |
22.00 3100.00 1.12 0.50 0.81 1.16 0.74 0.18 0.85 0.48 0.16 0.55 0.30 250.00
|
21.00 3200.00 1.01 0.45 0.76 1.07 0.68 0.16 0.80 0.46 0.16 0.55 0.30 250.00
|
As per breed the requirements of nutrients are slightly different for broiler birds.
Conclusion:
Each of these feed additives has their specific benefits. There is no debate that several feed additives can bring many changes in the animal’s response to nutrients and disease challenge. Since inconsistent effects have been seen while using the poultry feed additives. So Further research is needed to not only identify new hope for poultry feeds additives but also need to recognize that how combinations of these additives can be used to improve the efficiency of poultry production. Work is required to minimise their negative effects if not used correctly or if they interact with other additives or feed ingredients. Systematic approach is required to explain the efficacy and mode of action for each of type and dose of additives. Approvement of various feed additives for use is important. After that they should be utilized as directed with inclusion levels and duration of feeding. They should also be specific for the age of birds being fed. Non antibiotic growth promoters such as organic acids and probiotics should be used. Safety should be in mind to reduce the feed industry’s impact on the environment.
Dr. Manash Dash, Poultry Consultant, Kolkata.
Compiled & Shared by- Team, LITD (Livestock Institute of Training & Development)
Image-Courtesy-Google
Reference-On Request.