Surgical management of incised wound in a horse using disposable stainless steel skin staples
Dr.N.Gurunathan1*, Dr. Ravivarman2, Dr.Bhuvanesh kumar2, Dr.N.Aruljothi3
1*Assistant professor, 2M.V.Sc. graduate, 3Professor & Head
Department of veterinary surgery & radiology, Rajiv Gandhi institute of veterinary education and Research, Puducherry – 605009
Summery
A four-year-old female crossbred kathiwadi horse was presented to department of veterinary surgery and radiology, RIVER, puducherry with the history of wound on the chest. on clinical examination an incised wound involving skin and muscles was observed at the chest. All the physiological and hematological parameters were within the normal range. The wound was aseptically prepared and closed using disposable stain less steel skin staples. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and tetanus toxoid were administered postoperatively. On 10th post-operative day, the wound healing was noticed and the staples were removed and the animal made an uneventful recovery.
Keywords: wound, skin staples and horse
Introduction
Wounds are common in horses. Due to the nature of horses and its environment wounds may occur at any parts of the body. The common causes of the wounds may be due to injury caused by fances, wires, thorns etc. wounds on examination may should the level of involvement of different tissues. Immediate attention is needed for wounds involving blood vessels. Following the initial triage of the wound, proper cleaning and administration of anti-inflammatory is necessary to reduce pain and swelling (caston, 2012).
Materials and method
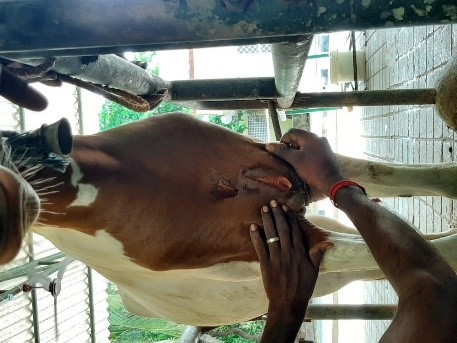
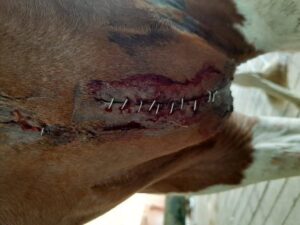
A four year old female crossbred kathiwadi horse was presented with a history of incised wound due to a sharp fence in the stable and was presented immediately to surgery unit, VCC, RIVER, Puducherry. On clinical examinations the feeding, voiding habits and rectal temperature and haematological parameters were within the normal range. On physical examination, an incised wound of around 6 cm length was observed at the chest region which involves skin and muscles (figure.1). The wound site was prepared aseptically and the wound edges were debrided. The wound was irrigated with povidone iodine diluted in normal saline. The muscles were sutured by simple continuous pattern using vicryl size 0. The skin was apposed using a disposable stainless steel skin staples (figure.2). The site was protected with povidone iodine gauze and dynafix bandage was applied. Postoperatively inj. Streptopenicillin @ 10mg/kg B.wt intramuscular for 5 days and inj. Melxicam @ 0.2mg/kg B.wt. intramuscular was for 3 days. Inj. Tetanus toxoid was administered post surgery. Dressing of the owund site was done on 5th and 8th postoperative day. On 10th postoperative day healing of the surgical site was observed and the skin staples were removed using staple remover. Complete healing of the surgical site with less scar formation was noticed and the animal made an uneventful recovery.
Result and discussion
Complete healing of the wound with proper apposition of the wound edges were brought by disposable skin staples (Premsairam et al., 2018) The surgical site showed no contamination and dry surgical site with no discharges or wound dehiscence. The application of disposable stainless steel skin staples were easy and was accepted by the animal and was easy to remove with out causing any pain to the animal. Less scar formation was observed at the surgical site after staples removed at 10th postoperative days (Gurunathan et al., 2019).
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful to Dean, RIVER, Puducherry for providing all the necessary facilities to conduct the study.
Reference
Caston, S.S. (2012). Wound care in horses. Veterinary clinics of north america: Equine practice, 28(1), 83-100.
Gurunathan N, Aruljothi N, Udayakumari B, Balagopalan TP. (2019). Surgical Management of fibropapiloma of teat in a cow- a case report, International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Science, 8(11):85-91.
Premsairam C, Aruljothi N, T.P.Balagopalan, R.Kumar and R.M.D.Alphonse. (2018). Surgical management of fibrosarcomaof teat in a cow – A case report. International Journal of Current Microbiology Applied Science, (2018) 7(6): 282-286.
Figure.1. incised wound at chest region
Figure.2. application of skin staples using disposable skin stapler
Figure.3. Stainless steel staples applied to skin for closure