The Science Behind Tail Wagging : Interpreting Tail Wags in Dogs
A wagging tail is a form of dog communication. Dogs wag their tails to tell us something about how they’re feeling, just as they do with other forms of body language.
What does a wagging tail mean?
When your dog wags his tail, is he telling you that he’s happy? Not necessarily! Canines know many variations of the “tail wag” and they all mean different things. In fact, a wag of the tail is one of the best methods of communication in the canine kingdom.
Like human infants, dogs must learn their language. Pups aren’t born knowing what a wagging tail means any more than a newborn baby understands words. But when a pup is about a month old, he recognizes the need to communicate with his mother and siblings, so he picks up the lingo. The pup wags his tail to tell his littermates that he’s tired of playing or to tell his mother that he’s hungry.
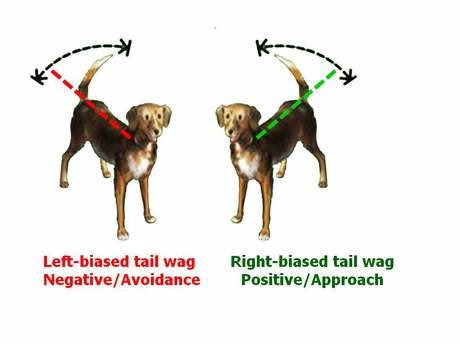
When humans see a dog wagging its tail, we pretty much equate that with a happy dog. It turns out that a dog’s tail may be much more expressive than we realize. Research has shown that happy dogs tend to wag more to the right, while anxious dogs go more to the left.
Why do dogs wag their tails to communicate?
Words are the basis of human communication, so people are good listeners. Dogs, on the other hand, are watchers. Lacking a verbal vocabulary, dogs communicate broader messages with body language by taking a certain stance, moving their ears, furrowing their brow, shifting their eyes or wagging their tails.
Tail wagging works well for dogs. Since canine vision is attuned more to movement than to colors or details, dogs readily discern different tail wags. Evolution has also helped by producing tails that are more visible. Some tails have color variations such as dark or light tips, some are lighter on the underside, and some are really bushy. All of these traits accentuate the tail wag and enhance communication.
What messages does a wagging tail communicate?
Before we learn to speak “tail,” we must recognize that the neutral or natural position of a dog’s tail varies by breed. Most dogs have tails that hang down near their heels when they are relaxed. But some dogs, like Beagles, hold their tails more vertically. Others, like Greyhounds and Whippets, curl their tails under their bellies. Still others, like Pugs and Boston Terriers, have tails that coil tightly against the body and don’t wag at all.
Tail position may indicate:
- Preparedness or agitation. When dogs are alert, they stand with their ears up and tails raised. This posture indicates that they are watching and ready to confront whatever caught their attention.
- Negotiation. When a dog suddenly stops wagging his tail and freezes, it may mean that he wants divert a threat without being aggressive. Many dogs do this when petted by strangers, to communicate that they don’t want to interact with them.
- Aggression. When a tail moves from a neutral position to a vertical one or arches over the back, it indicates that the dog may be aggressive. The higher the tail, the greater the threat. This high tail position also releases more of the dog’s scent from the anal glands, announcing the aggressive dog’s arrival and marking his territory.
- Submission. When a tail moves from the neutral position to a lower one, the dog is submissive and is not a threat. If the tail is tucked tightly between the rear legs, the dog is scared. He perceives a threat and is asking not to be harmed. This lower tail position reduces the amount of scent emitted from the anal glands and allows the dog to remain in the background or fly under the radar.
- When a dog is curious about something, she holds her tails straight out in a horizontal position.
- When a dog is happy, he holds his tail in a neutral or slightly raised position and adds a healthy wag.
The rate at which a tail moves adds further meaning to canine communication.
Wagging speed may indicate:
- The faster the wag, the more excited the dog. A tail wag may range from very slow to extremely rapid (known as flagging). Sometimes the dog’s tail wags so fast that it appears to vibrate.
- A dog that is tentative about meeting a new person or another dog may wag his tail ever so slightly to indicate that he is insecure.
- A dog that is very friendly may wag his tail more freely and even wiggle his hips at the same time.
- When a dog wags his tail very fast while holding it vertically, he may be an active threat. Remember that a person can get bitten by a dog that is wagging its tail!
Canine “tail talk” is so complex that even the direction of the wagging is significant. Studies show that dogs wag their tails to the right when they are happy or confident and to the left when they are frightened. Interestingly, there is a scientific reason for this.
The left side of the brain controls movement on the right side of the body and vice versa. Therefore, the left brain is engaged when the tail wags to the right and the right brain causes the tail to move to the left. Since the left side of the brain is associated with positive feelings like love and serenity, a happy dog wags his tail to the right. Conversely, the right half of the brain is associated with negative feelings like fear and depression, so a frightened dog wags his tail to the left.
Can tailless dogs communicate?
Dogs without tails communicate, but they have limitations. They may approach other dogs or people cautiously to avoid miscommunication. They depend on other aspects of body language such as ear position, facial expression, and stance to communicate their intentions.
As humans, we depend on verbal communication with one another to get our point across. While they do vocalize some of their feelings, dogs rely a lot more on other means of communication.
Dogs might pass along information to other dogs using:
- Pheromones
- Smells from glandular secretions
- Vocalizations including barks, whines, and growls
- Body posture
- Eye and ear position
- Gestures and subtle visual cues such as raising hair
Humans are not used to being on the lookout for some of less obvious ways a dog might communicate, but that doesn’t mean we can’t learn!
What canine tail wagging really means?
Why Dogs Wag Their Tails
Dogs wag their tail to communicate with humans and other animals. Often, it seems fairly obvious what the dog is trying to tell you when it wags its tail. Most people look at a dog with a wagging tail and assume it is happy. While this is usually true, there are times when a dog wags its tail just before it becomes aggressive. It is important that you pay attention to how the dog is holding its tail when it’s wagging it. Where the tail is and the way a dog holds its body while it’s wagging it can give you a clue about what it is trying to communicate. You should also pay attention to other signs in the dog’s body language.
Happy Wagging
Is the dog’s tail relaxed and moving back and forth? Is its body moving along with the wagging? If a dog is wagging its tail and the rest of its body seems relaxed or is moving along with the wagging, you are probably dealing with a happy, comfortable dog. Happy, relaxed tail wagging is usually accompanied by a happy facial expression. A happy dog usually has bright eyes, a relaxed open mouth, and possibly a gentle pant. Fast tail wagging with other happy signals usually means the dog is excited.
Alternative Reasons
Is the dog’s tail high and moving in back and forth motion while the dog’s body remains fairly erect and rigid? If a dog is holding its body erect and rigid while wagging its tail, it may be telling you that it’s feeling territorial or uncomfortable with something that is going on around it. The tail may be low and wagging slowly, usually because the dog is hesitant about something. Or the dog’s tail may be held high and moving back and forth, narrowly but rapidly. This discomfort can be a precursor to aggression. This is one reason people sometimes report that a dog was wagging its tail just before it bit someone. So, if you encounter a dog you don’t know who is wagging its tail, check out what the rest of its body language is telling you before you approach. It’s better to be safe than to get bitten by a dog.
Left and Right Tail Wagging
Does it matter which direction a dog’s tail wags? One study shows it might matter when it comes to dog-to-dog communication.1 Researchers found that dogs had different emotional responses depending on whether another dog’s tail was wagging to the left or right. Dogs observing another dog wag to the right seemed to become relaxed. Dogs watching another dog with a left tail wag exhibited signs of nervousness, stress, or anxiety. This study shines some light on the way dogs interact with one another.
Reading Wag Speed
The speed of a dog’s wagging tail might also give you an indication of his mood-
- Quick wag: A short wag usually happens during greetings when a dog is feeling tentative.
- Big, broad wag: This indicates a friendly dog who is not threatening anyone.
- Slow, reluctant wag:This might indicate a dog who is feeling anxious. Other signs of anxiety include avoiding eye contact, refusing food or ignoring what’s happening around him.
- Tiny, high-speed wag: A tail that moves in short, vibrating bursts can be a sign a dog is about to run or fight. Be careful!
Why Dogs Wag Their Tails
A tail is worth a thousand words when it comes to dog language. Dubbing a tail wag as a signal of happiness is simply an overgeneralization we tend to make as a two-legged species. Why dogs wag their tails amounts to a more complex communication strategy.
The next time you see a pooch wagging her tail, pay a little closer attention to the details. Observing the specifics of a pet’s wag can help you understand what point your pup is trying to convey.
For instance:
- A high back and forth wag is a sign of happiness
- A horizontal tail indicates your dog is curious about his surroundings
- A tucked, wagging tail shows worry or insecurity
- A vertical tail, even if wagging, can indicate aggression
- Wagging to the right supports a happy message
- Wagging to the left may indicate your pet is feeling scared or worried
- A dog who carries her tail high all the time may be confident, spreading anal gland scent
- Low tail carriage may mean a dog is trying to lay low
- The faster the wag, the more passionate the message
Interestingly, dogs who do not have tails need to be much more cautious mingling with their canine counterparts, as they can’t convey their message as well.
A dog’s tail helps to provide balance, but is also a key player in canine communication. With a little practice, you can understand your pet’s tail a bit better, helping you to understand and reinforce good behavior in your faithful companion even better.
More Than Just Communication
Apart from the tail’s wagging being used for effective communication and expression of emotion, tails are also used for helping the dog stand or run properly. It assists in providing balance to the dog. When dogs run at high speed, either playfully or after something/ someone, they use their tails to help them stabilise and not fall while running so fast. Not just on the ground, but dogs use their tails while swimming too! It gives them the push or momentum required to stay above water.
This was all about the tail wag and how dogs use it differently. It is up to us to understand and respect the emotions a dog expresses. Never misinterpret a dog wagging its tail as someone who wants to be petted. Often dogs wag their tails while they are engaging or interacting with the environment around them.
Compiled & Shared by- Team, LITD (Livestock Institute of Training & Development)
Image-Courtesy-Google
Reference-On Request.