By Dr Rakesh kr.Singh,TVO.Motihari
Feed resource availability in the country for livestock is not adequate and the gap between the requirement and availability is widening. Further, the dry fodder which are the major feed resource characterized by low intake and digestibility due to the high fibre, lignin and silica content. Total crop residues availability in the country from different crops is estimated to be 315 million tons including straw, stover, kadbi etc. Hence, feeding of fibrous crop residues fails to even fulfill the maintenance requirement of the animal. Different methods have been employed for improving the quality of fibrous crop residues and making them suitable for the feeding of livestock. Alkali treatment is noteworthy where caustic soda, lime, ammonia, urea or urine may be used for the purpose but have some serious limitations at the farmer’s doorstep like cost, toxicity, trained staff etc. However, the use of urea is comparatively safe and has the distinct advantage of universal availability, less risk and low cost as compared to ammonia or alkali treatment. The urea treatment technology is simple and has great potential for adoption at farm-gate level for enhancing the utilization of poor quality roughages.
Mechanism of action:
Urea treatment of straw and stover works on the principal of ureolysis and alkali action on the cell through dissolving the structural carbohydrates especially the hemicellulose, swelling of the plant matter in an aqueous environment, reducing the physical strength of cell. Urea treatment of straw leads to an increase in intake (20-25%; 1-2 units), digestibility (10-15%; 5-6 units) and energy availability to the host animal which otherwise would have been wasted. Urea treatment also enriches the straw for its protein content (up to 9-10%; 5-6 units). On hydrolysis of 1 mol urea (60 g) generates 34 g of ammonia, thus 4% of urea used for the straw treatment will allow the production of 2.67 kg of rd rd ammonia of which 2/3 is labile and lost and rest 1/3 acts on cell wall.
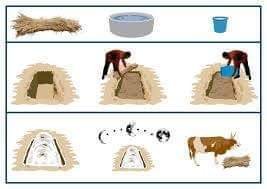
Process: Simple steps of urea treatment is given below
1.Chaffing/thrashing of crop residue/stover by chaff cutter to 1-2” size
II Collect/store the chopped straw at a safe and dry place till further use
III Weigh 100kg straw for urea treatment
IV Make the urea solution by dissolving 4 kg urea into 40 liter water
V Spread the straw layer on polythene or tarpaulin sheet
VI Fill the urea solution in a container and spray over straw layer uniformly
VII Fill the urea treated straw immediately in an airtight bag and close it properly
. VIII Ensure the complete air tightness of bag and keep it for at least 2 weeks
IX Open the bag; remove top 1-1 ½ inch layer and offer the straw to livestock S
Many times it happened that remaining residues in farm are burned without using their potential in dairy farming. Waste of crop like wheat straw, Rice straw, Gram straw can be used as feed of animals but it need treatment.
Reason for treatment of crop residues
• It is tasteless.
• Some crop residues are having micro spines which cause injury to soft tissues in the mouth of animals.
• Its energy as well as protein value is inferior.
• Some of them are deficient in minerals.
It has seen that wheat straw or rice straw are available in abundant quantity as crop waste & many farmers used to burn it as traditional practice, so it is necessary to use it as a feed for animals after having treatment of following ingredients.
SR. INGREDIENTS QUANTITY
1 Wheat straw / rice straw/maize stovers etc. 100 KG
2 Urea 1.5 KG (1.5%)
3 Mineral Mixture 1 KG (1%)
4 Salt (Big Granules) 1 KG (1%)
5 Jaggery (If not available, waste flour in flour mill can be used) 3 KG (3%)
6 Water 30 – 40 Ltrs.
Treatment method
• Dissolve urea in correct concentration (as above) in water (1.5 kg urea in 30-40 litres of water)
• Then also add Salt, Mineral mixture & Jaggary (or Flour) in urea dissolved water to become concentrate single solution.
• Make a layer of 6 inches of wheat or rice straw and sprinkle concentrates solution on it equally. Again mix this layer thoroughly & make a heap. Once again make a layer of 6 inch of this wheat straw and sprinkle the concentrated solution.
• Make a heap & press it with the help of hand so that all air will expel out form heap. Then cover it with plastic paper for 2 hours.
• Then use it for feed to animals.
Facts for urea/ammonia treatment
• Urea provides readymade protein source for animals
• Salt & mineral mixture provide essential mineral for animals which are lacking in crop residues.
• Jaggery or flour provides taste to straw as straw is tasteless.
• Water soften the spine as well as harder part in straw so it is easy to fed on it & may not cause any injury to soft tissues in mouths of animals.
Care to be taken for urea treated straw
• Do not exceed the urea concentration for wheat straw more than 1.5 % for 100 kg of straw. If it will increase then there may be danger of urea poisoning to animals.
• Care to be taken to dissolve each granules of urea in water thoroughly.
• Use this urea treated straw immediately after 2 hours of treatment. Do not store treated material for more than 8 hours.
• Daily use fresh treated straw for animals & for each animals use this straw 4-6 kg only for high producing dairy animals .If the animals are not in production then it is physible to use 7-8 kgs of treated wheat straw for feeding animals.
• Mix treated wheat straw in chaffed green as well as dry fodder so that animal can not use its selective behavior of feeding.
• UREA TREATMENT OF PADDY STRAW WITHOUT USING JAGGERY.
•
• Benefit:
• 1. Treated paddy straw has enhanced nutritive value than the untreated paddy straw.
• 2. Treaded paddy straw is liked by cattle.
• 3. Increase palatability.
• 4. Intake will increase
• 5. Maintained the health quality.
• Items:
•
• 1. 100 kg paddy straw
• 2. 40 liters of water
• 3. 4 Kg. Urea.
• 4. Polythene sheet
• 5. Water cane
• 6. Bucket etc.
• Procedure:
•
• 1. Polythene sheet should be spread over on the selected site.
• 2. The one fourth paddy straw will be spread over the polythene sheet
• 3. The water urea solution will be sprinkle over the paddy straw and mixed properly.
• 4. Then next one fourth paddy straw will be spread over and again urea solution will be sprinkle
till completion of the straw.
• 5. The treated straw will be airtight and kept for 21 days.
•
• Precaution:
• 1. The calf of below six month will not be fed with treated straw.
• 2. The pregnant cattle are also not being fed with treated straw.
• 3. The fungal growth straw should not be taken for UTPS
• 4. The treated straw will be fed after exposure of air for at least 10 minute.
• 5. The starting quantity of UTPS should be regulated from lesser quantity to higher in periodic
manner.
• CHAFF CUTTER
• 1. Wastage of fodder reduces.
• 2. Increase palatability.
• 3. Digestibility increase.
• 4. Easy to handle fodder quantity.
•
• Precaution:
• 1. Use by children is avoided.
• 2. May be kept under lock and keys.
• 3. Regular mobilization for easy running.
NB: Reference on request.