Uterine torsion: Causes, symptoms and management strategies
Pawan Kumar Sharma
MVSc, Department of Veterinary Gynaecology and Obstetrics, CVAS, RAJUVAS, Bikaner, Rajasthan.
*Corresponding and presenting author Email – pawansharma6596@gmail.com
Introduction
Uterine torsion, a condition characterized by the twisting of the uterus along its longitudinal axis, is most commonly affects buffaloes and cattle worldwide. It can lead to severe complications during pregnancy and parturition, resulting in economic losses for farmers. Uterine torsion most commonly occurs during late gestation or near parturition. It is maternal cause of dystocia. Uterine torsion exerts considerable stress on the animal and if not treated promptly, it can lead to toxemia followed by dam as well as fetal mortality. This article deals with the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for uterine torsion.
Causes
- Fetal Movements: The vigorous movements of the developing fetus within the uterus can sometimes lead to the twisting of the uterus, especially during the later stages of pregnancy.
- Uterine Abnormalities: Structural abnormalities of the uterus, such as a pendulous uterus or elongated horns, can predispose to uterine torsion.
- Lack of Exercise: Inadequate exercise or close confinement in small spaces can increase the risk of uterine torsion.
Symptoms
Animal with uterine torsion often exhibit a visibly distended abdomen due to the twisted uterus and may show a decrease in feed intake. Animal experiencing uterine torsion may display signs of restlessness, pawing at the ground, kicking of the abdomen with hind legs on the side of the pain and frequent lying down and getting up. Uterine torsion can impede the progress of labor, leading to prolonged calving or even stillbirth.
Diagnosis
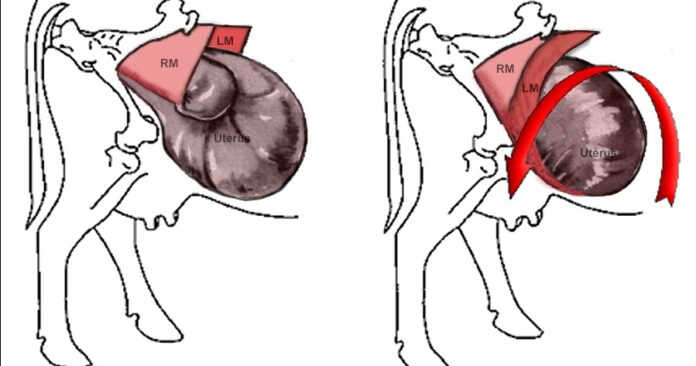
Prompt clinical examination is crucial for good prognosis of uterine torsion. Uterine torsion can diagnose by the help of symptoms along with rectal and vaginal palpation. Vaginal examination reveals twisting of the vaginal wall in the side of torsion. In case of pre cervical uterine torsion pervaginal examination is not useful in diagnosis. On rectal palpation, the broad ligament on the side of torsion is twisted along with the uterus and the opposite broad ligament becomes stretched.
Treatment
- Manual Correction: In cases of mild to moderate degree uterine torsion where obstetrician can touch the fetus. Manual repositioning of the fetus can be done through the cervix with the help of caemmerer’s torsion fork or kuhen crutch.
- Rolling of animal: Uterine torsion can be corrected by rolling the animal while uterus remain static. In case of mild degree of uterine torsion sudden rolling of animal might be effective. During sudden rolling rapid rotating body of the animal overtakes the slowly rotating gravid uterus which helps in repositioning of uterus. In Schaeffer’s method of uterine torsion correction the fetus is immobilized using a plank that is held in an inclined position on the animal’s abdomen after casting the dam in lateral recumbency to the side of torsion. Three individuals sustained pressure on the plank’s edge by standing on it while the animal was rolled to the other side. The modified Schaffer’s approach, which involves applying pressure from a person, was employed since the plank kept slipping over while the animal was being rolled. Three to four people placed pressure on the end of the plank that touched the ground by standing on it, while one person put pressure on the other end of the plank.
- Surgical Intervention: Severe uterine torsion or cases where manual correction or rolling of animal is unsuccessful may require surgical intervention. Laparotomy can be performed to restore the uterus to its normal position.
- Post-treatment Care: Following successful correction, animal should be monitored closely for any signs of infection or uterine damage. Adequate fluid therapy, pain management and appropriate antibiotics may be prescribed to ensure a smooth recovery.
Prevention Strategies
- Exercise and Management: Encouraging regular exercise and providing sufficient space for movement can reduce the risk of uterine torsion.
- Proper Nutrition: Maintaining a balanced and adequate diet throughout pregnancy supports the overall health and strength of the buffalo, reducing the chances of uterine torsion.
- Timely healthcare: Regular veterinary check-ups during pregnancy allow for early detection of any potential issues, including uterine torsion.
Conclusion
Uterine torsion poses a significant challenge in reproductive health and can have detrimental effects on both the animal and the farmer. Recognizing the causes, identifying symptoms, and implementing appropriate management strategies are vital in minimizing the occurrence and severity of uterine torsion. By adopting preventive measures and seeking timely veterinary care, buffalo farmers can ensure the well-being of their herds and optimize reproductive outcomes.