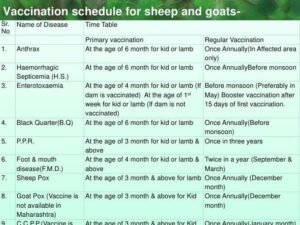
Vaccination schedule for goats
| S.No. | Name of Disease | Time Table | |
| Primary vaccination | Regular Vaccination | ||
| 1. | Anthrax | At the age of 6 month for kid or lamb | Once Annually (In Affected area only) |
| 2. | Haemorrhagic Septicemia (H.S.) | At the age of 6 month for kid or lamb | Once Annually Before monsoon |
| 3. | Enterotoxaemia | At the age of 4 month for kid or lamb (If dam (female goat) is vaccinated)
At the age of 1st week for kid or lamb(If dam is not vaccinated) |
Before monsoon (Preferably in May). Booster vaccination after 15 days of first vaccination. |
| 4. | Black Quarter (B.Q) | At the age of 6 month for kid or lamb | Once Annually (Before monsoon) |
| 5. | P.P.R. Peste Des Petits Ruminanat | At the age of 3 month for kid or lamb & above | Once in three years |
| 6. | Foot & mouth disease (F.M.D.) | At the age of 4 month for kid or lamb & above | Twice in a year (September & March) |
| 7.. | Goat Pox | At the age of 3 month & above for Kid | Once Annually (December month) |
| 8. | C.C.P.P | At the age of 3 month & above for Kid or lamb | Once Annually (January month) |
Disease Prevention/Control:
- Clean sanitary conditions of poultry sheds and equipment, balanced feed, fresh clean water, healthy chicks are essential to prevent diseases.
- Avoid entry of visitors to farm, especially inside the If visitors come, ask them to dip their feet in a disinfectant solution, wash and clean hands and to wear apron/boots provided by the farm.
- Use proper vaccination schedule.
- Use high quality vaccines purchased from reputed Keep vaccines in cool, dry conditions away from sunlight.
- Any left-over vaccine should be properly disposed Vaccines should not be used after their expiry date is over.
- Any dead bird should be immediately removed from the shed and sent to laboratory for post-mortem or buried/burnt suitably away from the poultry farm.
- The waste of farm should be suitably disposed of.
- Any bird showing advanced signs of a disease should be removed from the shed and It can be sent to laboratory for diagnosis.
- Birds showing advanced signs of a disease should be shown to a qualified veterinarian and suitable medication/treatment be given as per his/drug manufacturers recommendations.
- Poultry manure, if infected, can spread disease, from one batch to Keep the litter dry, remove it after flock is sold and dispose the manure properly and quickly.
- Keep proper records on mortality and its causes and the treatment given to Dates of vaccination for each flock should be properly recorded.
- Rats are important carriers of poultry Avoid rats. Use suitable rat poisons/rat traps.
- Many poultry medicines can be given in drinking When medication is to be given, remove the waterers in poultry sheds on the previous evening. Next morning give medicine in measured quantity of water, so that entire medicine will be quickly consumed and there will be no wastage of medicines.
- Mild infection of disease may not cause mortality but it will reduce growth. Keep sample record of body weight and mortality rate. Study the possible causes, if weight is low take steps to improve the management of the subsequent A Constant visit and analysis of records/results is necessary to keep up the efficiency in farming.
Vaccination and Annual Health Calendar for Sheep and Goat
VACCINATION CALENDAR FOR SHEEP & GOAT




